LMS for Education Market Size, Share, and Trends Analysis Report
CAGR :

| Market Size 2023 (Base Year) | USD 10.73 Billion |
| Market Size 2032 (Forecast Year) | USD 43.68 Billion |
| CAGR | 16.88% |
| Forecast Period | 2024 - 2032 |
| Historical Period | 2018 - 2023 |
LMS for Education Market Insights
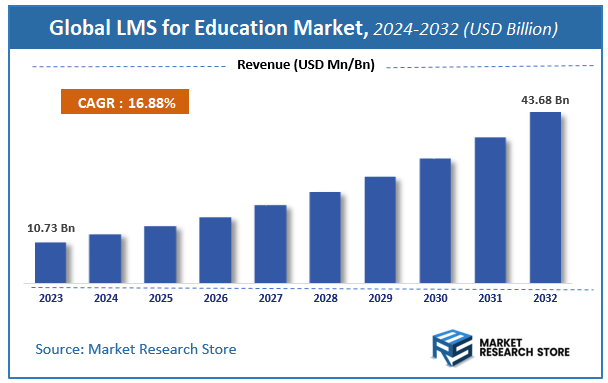
According to Market Research Store, the global LMS for education market size was valued at around USD 10.73 billion in 2023 and is estimated to reach USD 43.68 billion by 2032, to register a CAGR of approximately 16.88% in terms of revenue during the forecast period 2024-2032.
The LMS for education report provides a comprehensive analysis of the market, including its size, share, growth trends, revenue details, and other crucial information regarding the target market. It also covers the drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges till 2032.
To Get more Insights, Request a Free Sample
Global LMS for Education Market: Overview
A Learning Management System (LMS) for education is a digital platform designed to plan, deliver, manage, and assess learning processes in academic institutions. It enables educators to create and share course content, track student progress, conduct assessments, and foster communication and collaboration among students and teachers. LMS platforms are used in schools, colleges, and universities to support both in-person and remote learning. These systems often offer features like virtual classrooms, quizzes, discussion boards, grading tools, and analytics. By centralizing educational content and facilitating streamlined administration, LMS platforms enhance teaching efficiency and provide students with greater flexibility in accessing educational resources.
Key Highlights
- The LMS for education market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 16.88% during the forecast period.
- The global LMS for education market was estimated to be worth approximately USD 10.73 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a value of USD 43.68 billion by 2032.
- The growth of the LMS for education market is being driven by increased internet penetration, growing reliance on e-learning, and the need for scalable education solutions.
- Based on the user type, the higher education institutions segment is growing at a high rate and is projected to dominate the market.
- On the basis of deployment model, the cloud-based LMS segment is projected to swipe the largest market share.
- In terms of learning paradigm, the blended learning segment is expected to dominate the market.
- Based on the industry vertical, the education segment is expected to dominate the market.
- In terms of functionality, the content management segment is expected to dominate the market.
- By region, North America is expected to dominate the global market during the forecast period.
LMS for Education Market: Dynamics
Key Growth Drivers:
- Increasing Adoption of Online and Blended Learning: The shift towards online and blended learning models in schools, colleges, universities, and vocational training centers, accelerated by the experiences of recent years, is a primary driver for LMS adoption. This is particularly evident in urban and semi-urban areas like Dombivli with growing internet penetration.
- Demand for Personalized and Flexible Learning: LMS platforms enable educators to deliver personalized learning experiences, track student progress, and offer flexible learning pathways, catering to diverse learning needs and paces.
- Need for Efficient Content Management and Delivery: LMS solutions streamline the creation, organization, and delivery of educational content (videos, documents, assessments), reducing administrative overhead for educators.
- Government Initiatives Promoting Digital Education: Government policies and funding aimed at promoting digital education infrastructure and online learning platforms, both nationally in India and within Maharashtra, are boosting LMS adoption in educational institutions.
- Growing Emphasis on Data-Driven Education: LMS platforms provide valuable data and analytics on student engagement, performance, and learning outcomes, enabling educators and institutions to make data-informed decisions for curriculum improvement and student support.
- Accessibility and Scalability: LMS solutions offer increased accessibility to education, reaching students in remote areas or those with mobility challenges. They also provide scalability to accommodate growing student populations without significant physical infrastructure expansion.
Restraints
- High Initial Implementation Costs: The cost of implementing and customizing a comprehensive LMS, along with the associated training and support, can be a significant financial barrier for some educational institutions, especially smaller schools and colleges in regions like Dombivli.
- Integration Challenges with Existing Infrastructure: Integrating a new LMS with existing student information systems (SIS), enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and other legacy IT infrastructure can be complex and time-consuming.
- Resistance to Change from Educators and Students: Some educators may be resistant to adopting new technologies, requiring adequate training and support to ensure effective utilization. Similarly, students with limited digital literacy might face initial challenges.
- Dependence on Reliable Internet Connectivity and Digital Devices: The effective use of an LMS requires reliable internet access and suitable digital devices for both educators and students, which can be a limitation in areas with poor infrastructure or for students from lower socioeconomic backgrounds.
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns: Handling sensitive student data within an LMS raises concerns about data privacy, security breaches, and compliance with relevant regulations. Robust security measures and adherence to data protection laws are crucial.
Opportunities
- Cloud-Based LMS Solutions: Cloud-based LMS platforms offer scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of maintenance, making them attractive to educational institutions of all sizes, including those in developing regions like India.
- Mobile Learning (m-Learning) Integration: Optimizing LMS platforms for mobile devices caters to the increasing use of smartphones and tablets by students, enabling learning on the go.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Incorporating AI-powered features for personalized learning recommendations, automated grading, and intelligent tutoring within LMS platforms can enhance their effectiveness.
- Focus on Gamification and Interactive Content: Integrating gamification elements and interactive content creation tools within LMS platforms can increase student engagement and motivation.
- Development of Specialized LMS for Niche Educational Segments: Creating tailored LMS solutions for specific educational sectors like vocational training, corporate learning, or early childhood education can address unique requirements.
- Partnerships with Content Providers: Collaborating with educational content creators to offer integrated and high-quality learning resources within the LMS can enhance its value proposition.
- Growth in the Indian Market: With a large and growing student population and increasing government focus on digital education, India, including urban centers like Dombivli, presents a significant growth opportunity for LMS providers.
Challenges
- Ensuring Accessibility and Equity: Bridging the digital divide and ensuring equitable access to LMS platforms and digital resources for all students, regardless of their socioeconomic background or location, remains a significant challenge, particularly in a diverse country like India.
- Maintaining Data Security and Privacy: Robust security measures and compliance with evolving data privacy regulations are crucial to protect sensitive student information within LMS platforms.
- Providing Adequate Training and Support: Offering comprehensive training and ongoing technical support for both educators and students is essential for the successful adoption and effective use of LMS platforms.
- Ensuring Quality of Online Learning Experiences: Maintaining the quality and engagement of online learning experiences compared to traditional face-to-face instruction requires careful pedagogical design and effective use of LMS features.
- Adapting to Evolving Educational Needs and Pedagogies: The LMS must be flexible and adaptable to support evolving educational needs, new pedagogical approaches, and emerging learning technologies.
- Managing the Proliferation of EdTech Solutions: Educational institutions face the challenge of selecting the right LMS from a growing number of EdTech solutions and ensuring interoperability with other educational tools.
LMS for Education Market: Report Scope
This report thoroughly analyzes the LMS for Education Market, exploring its historical trends, current state, and future projections. The market estimates presented result from a robust research methodology, incorporating primary research, secondary sources, and expert opinions. These estimates are influenced by the prevailing market dynamics as well as key economic, social, and political factors. Furthermore, the report considers the impact of regulations, government expenditures, and advancements in research and development on the market. Both positive and negative shifts are evaluated to ensure a comprehensive and accurate market outlook.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | LMS for Education Market |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 10.73 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2032 | USD 43.68 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 16.88% |
| Number of Pages | 175 |
| Key Companies Covered | Civica, Companion, Ex Libris, Follett, Sirsidynix, Blackboard, Moodle, Desire2Learn, SAP, Saba Software, Sumtotal Systems, eCollege, WebCT, Edmodo, McGraw-Hill, Pearson, GlobalScholar, Automatic Data Processing, Cornerstone OnDemand, Netdimensions, Oracle, Sungard, Jenzabar, Instructure |
| Segments Covered | By User Type, By Deployment Model, By Learning Paradigm, By Industry Vertical, By Functionality, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historical Year | 2018 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2024 to 2032 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
LMS for Education Market: Segmentation Insights
The global LMS for education market is divided by user type, deployment model, learning paradigm, industry vertical, functionality, and region.
Segmentation Insights by User Type
Based on user type, the global LMS for education market is divided into higher education institutions, k-12 schools, corporate training providers, and non-profit organizations.
In the LMS for education market, the most dominant segment by user type is Higher Education Institutions. These institutions widely adopt Learning Management Systems (LMS) to manage large-scale student bodies, offer online and blended learning courses, and support remote access to academic resources. The growth of distance learning programs and the integration of advanced digital tools such as AI-powered analytics and adaptive learning modules have further solidified the dominance of higher education in the LMS market. Universities and colleges also tend to invest more heavily in scalable, customizable LMS platforms to support diverse curricula and improve administrative efficiency.
Following closely are K-12 Schools, which represent the second most significant user segment. The adoption of LMS platforms in K-12 settings has surged, especially post-pandemic, as schools aim to ensure continuity of education during closures and beyond. LMS tools support student engagement, digital assignment management, and parent-teacher communication. However, budget constraints and the variability in digital infrastructure across school districts can impact the level of adoption.
Corporate Training Providers form the next segment, leveraging LMS platforms to deliver skill-based training, compliance education, and professional development programs. This user type benefits from features such as tracking employee progress, certification management, and content customization. Although not as dominant as higher education or K-12 schools in terms of volume, corporate users often demand more sophisticated features and pay higher premiums for specialized solutions, making this a valuable segment commercially.
Lastly, Non-Profit Organizations represent the least dominant segment. These entities use LMS solutions to educate their members, volunteers, or target communities, often in the context of awareness campaigns, humanitarian training, or social advocacy. Limited funding and fewer training participants compared to other segments constrain the growth and impact of this user type within the LMS market. Nonetheless, the push for digital transformation even in mission-driven sectors is encouraging modest growth in this area.
Segmentation Insights by Deployment Model
On the basis of deployment model, the global LMS for education market is bifurcated into cloud-based LMS, on-premises LMS, and hybrid deployment.
In the LMS for education market, the most dominant segment by deployment model is Cloud-Based LMS. This model has surged in popularity due to its scalability, ease of access, and lower upfront costs. Educational institutions increasingly favor cloud-based systems because they support remote learning, require minimal IT infrastructure, and offer real-time updates and support. The ability to access learning content anytime and anywhere aligns perfectly with the shift toward flexible and hybrid learning models, making this deployment method the clear leader in the market.
On-Premises LMS ranks as the second most dominant segment. While declining in relative popularity, it remains important for institutions that prioritize data control, customization, and security. Universities or organizations with the necessary IT capabilities may opt for on-premises deployment to integrate deeply with internal systems and maintain full ownership of their data. However, the higher costs of installation, maintenance, and upgrades often limit its appeal, especially for smaller institutions.
Hybrid Deployment is the least dominant segment but is gaining attention as a middle-ground solution. It combines the flexibility of cloud-based systems with the control of on-premises infrastructure. Institutions choosing this model aim to maintain certain sensitive operations locally while leveraging the scalability and accessibility of the cloud for other functions. Though currently the smallest segment, hybrid deployment is expected to grow as education providers seek balance between agility and data sovereignty.
Segmentation Insights by Learning Paradigm
Based on learning paradigm, the global LMS for education market is divided into blended learning, distance learning, self-paced learning, and instructor-led training.
In the LMS for education market, the most dominant segment by learning paradigm is Blended Learning. This model integrates both face-to-face classroom methods and online learning experiences, offering the best of both worlds. Educational institutions widely adopt blended learning because it provides flexibility for students while maintaining essential instructor-student interaction. The versatility of this approach allows educators to tailor the learning experience, use LMS features like assessments and analytics effectively, and adapt to both in-person and remote scenarios—making it the leading paradigm across user types.
Distance Learning holds the second most dominant position, propelled by the rise of fully online degree programs, MOOCs (Massive Open Online Courses), and global access to education. LMS platforms play a central role in facilitating asynchronous communication, content delivery, and student tracking for distance learners. This model gained massive momentum during the COVID-19 pandemic and continues to see sustained demand due to its ability to serve non-traditional learners, working professionals, and international students.
Self-Paced Learning ranks third, appealing to learners who value autonomy over their educational journey. LMS platforms that support this model allow users to progress through course material at their own speed, which is particularly valuable for professional development and microlearning scenarios. While widely used in corporate and continuing education settings, its application in traditional education is more limited, reducing its dominance in the broader LMS market.
Instructor-Led Training (ILT) is the least dominant segment in the context of LMS-based education. Though still essential for certain subjects and skills that require direct guidance, ILT often relies more heavily on real-time interaction and less on asynchronous LMS features. When supported by an LMS, ILT is typically enhanced through scheduling tools, attendance tracking, and resource sharing rather than serving as the core mode of delivery. As a result, its role in LMS adoption remains supplementary compared to more autonomous or hybrid learning approaches.
Segmentation Insights by Industry Vertical
On the basis of industry vertical, the global LMS for education market is bifurcated into education, healthcare, manufacturing, retail, and information technology.
In the LMS for education market, by industry vertical, the most dominant segment is unequivocally Education itself. Schools, colleges, universities, and other academic institutions are the primary drivers of LMS adoption. These organizations rely on LMS platforms to streamline course delivery, track student performance, and support hybrid or fully online learning environments. The demand in this sector is consistently high due to increasing digitalization of academic processes, government initiatives for e-learning, and a global push for accessible education.
Information Technology (IT) is the second most dominant vertical. IT companies leverage LMS platforms primarily for employee training, certification programs, onboarding, and continuous learning. The fast-paced nature of the tech industry demands constant skill upgrades, and LMS systems offer scalable, trackable, and customizable training environments suited to these needs. IT organizations also often develop or integrate advanced features such as gamification, analytics, and AI in their LMS usage.
Healthcare follows as the third-largest vertical. In this sector, LMS platforms are used to deliver ongoing medical education, compliance training, and certification for healthcare professionals. As regulations and medical practices evolve rapidly, LMS systems help hospitals, clinics, and medical institutions maintain up-to-date staff knowledge and ensure adherence to protocols. However, the complexity of medical training and reliance on hands-on learning limit complete LMS adoption to a degree.
Manufacturing ranks next, using LMS primarily for safety training, equipment handling procedures, and standard operating protocol dissemination. These companies benefit from LMS systems to ensure compliance with industrial regulations and to onboard new employees quickly. Yet, adoption in this sector tends to be more utilitarian and limited compared to IT or healthcare, leading to a less dominant role in the market.
Retail is the least dominant vertical in LMS adoption. Retail businesses use LMS platforms to train frontline employees, especially on customer service, product knowledge, and sales techniques. However, due to high employee turnover, limited training budgets, and reliance on short, in-person sessions, LMS usage is often minimal and less integrated into long-term strategies—making retail the smallest segment in this category.
Segmentation Insights by Functionality
On the basis of functionality, the global LMS for education market is bifurcated into content management, assessment & evaluation, reporting & analytics, collaboration tools, and mobile learning features.
In the LMS for education market, by functionality, the most dominant segment is Content Management. This core functionality forms the foundation of any LMS platform, enabling educators and administrators to create, upload, organize, and deliver learning materials in various formats such as documents, videos, SCORM packages, and interactive modules. The ability to manage curricula efficiently and provide structured content access is essential for both academic and corporate users, making content management the most utilized and indispensable functionality in LMS platforms.
Assessment & Evaluation comes next in dominance. LMS platforms offer built-in tools to create quizzes, assignments, exams, and performance evaluations. These tools are crucial for tracking learner progress, providing feedback, and supporting competency-based learning models. As education and training shift toward data-driven outcomes, assessment and evaluation functionalities are increasingly prioritized by institutions seeking measurable learning effectiveness.
Reporting & Analytics ranks third and is rapidly growing in importance. With the rise of personalized learning and administrative accountability, LMS platforms are now expected to offer dashboards, learner engagement metrics, course completion data, and predictive analytics. These insights help institutions identify at-risk students, improve curriculum design, and make informed decisions. While not as foundational as content or assessments, this feature is becoming a competitive differentiator.
Collaboration Tools such as discussion forums, messaging, shared workspaces, and virtual classrooms are also vital but slightly less dominant. These features support peer interaction, group learning, and instructor engagement—especially in blended and online learning environments. However, collaboration tools are sometimes replaced or supplemented by external platforms (e.g., Zoom, Slack, Teams), which can limit their usage within the LMS itself.
Mobile Learning Features are the least dominant but increasingly relevant. These functionalities allow learners to access courses, submit assignments, and receive notifications via smartphones or tablets. While mobile learning is essential for flexibility and accessibility—especially for remote or on-the-go learners—many LMS platforms still lag in offering fully optimized mobile experiences. As mobile adoption rises globally, this segment is expected to grow but currently remains the least mature among the listed functionalities.
LMS for Education Market: Regional Insights
- North America is expected to dominates the global market
North America is the most dominant region in the global LMS for education market. This leadership is driven by its well-established digital infrastructure, high technology adoption rates, and significant investments in education and corporate training. The region's enterprises prioritize employee development through structured learning paths, supported by LMS platforms integrated with advanced features such as artificial intelligence, analytics, and gamification. Educational institutions also adopt LMS tools to support blended learning environments and maintain compliance with regulatory standards, reinforcing the region’s stronghold in the market.
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the LMS for education market, characterized by rapid digital transformation and increased government support for e-learning. Countries such as China, India, and Japan are leading the adoption of LMS platforms to meet the educational demands of their large and diverse populations. Initiatives to improve digital literacy and workforce skill development are boosting the use of cloud-based and mobile-compatible LMS solutions. The region’s growing internet user base and emphasis on scalable, cost-effective learning tools are driving sustained market expansion.
Europe maintains a significant position in the LMS for education market, supported by a strong emphasis on lifelong learning, digital education integration, and regulatory compliance. Countries like Germany, the United Kingdom, and France are front-runners in deploying LMS systems across educational institutions and corporate environments. The demand for continuous professional development and advanced training methods is fostering LMS adoption, particularly in industries with strict training mandates and certification requirements.
Latin America is showing steady growth in the LMS for education market, driven by the need to enhance access to quality education and expand workforce development programs. Brazil and Mexico are leading the region in adopting LMS platforms for both academic and business training use. The increasing availability of digital devices and mobile connectivity is enabling broader adoption, especially in underserved and remote areas. LMS solutions in the region are often sought for their affordability and ability to deliver learning at scale.
Middle East and Africa are emerging players in the LMS for education market, with progress being made through government-led digital education initiatives and increased investment in learning technologies. Countries such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia are deploying LMS tools as part of broader national strategies to modernize education and improve workforce readiness. Despite infrastructure challenges in parts of the region, the growing availability of mobile internet and the young demographic’s demand for digital solutions are supporting the expansion of LMS adoption.
Recent Developments:
- In October 2024, Obrizum Group Ltd. partnered with Anthology Inc. to enhance Blackboard LMS with AI-driven personalization and advanced analytics. The collaboration aims to deliver adaptive learning experiences and deeper insights for Blackboard’s global users.
- In February 2024, Docebo integrated its LMS with Microsoft Viva Learning, enabling users to access training content directly within Microsoft Teams, streamlining the learning process.
- In January 2024, Blackboard partnered with Microsoft 365 to enhance integration with tools like Teams and OneDrive, improving the user experience and workflow for students and educators.
LMS for Education Market: Competitive Landscape
The report provides an in-depth analysis of companies operating in the LMS for education market, including their geographic presence, business strategies, product offerings, market share, and recent developments. This analysis helps to understand market competition.
Some of the major players in the global LMS for education market include:
- Civica
- Companion
- Ex Libris
- Follett
- Sirsidynix
- Blackboard
- Moodle
- Desire2Learn
- SAP
- Saba Software
- Sumtotal Systems
- eCollege
- WebCT
- Edmodo
- McGraw-Hill
- Pearson
- GlobalScholar
- Automatic Data Processing
- Cornerstone OnDemand
- Netdimensions
- Oracle
- Sungard
- Jenzabar
- Instructure
The global LMS for education market is segmented as follows:
By User Type
- Higher Education Institutions
- K-12 Schools
- Corporate Training Providers
- Non-Profit Organizations
By Deployment Model
- Cloud-Based LMS
- On-Premises LMS
- Hybrid Deployment
By Learning Paradigm
- Blended Learning
- Distance Learning
- Self-Paced Learning
- Instructor-Led Training
By Industry Vertical
- Education
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
- Retail
- Information Technology
By Functionality
- Content Management
- Assessment and Evaluation
- Reporting and Analytics
- Collaboration Tools
- Mobile Learning Features
By Region
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Rest of Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Table Of Content
Inquiry For Buying
LMS for Education
Request Sample
LMS for Education
