LTE Small Base Station Market Size, Share, and Trends Analysis Report
CAGR :

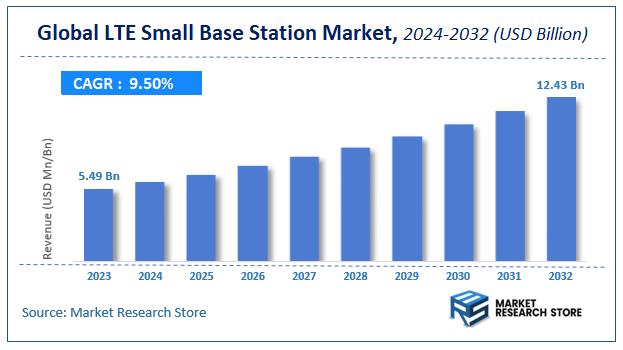
| Market Size 2023 (Base Year) | USD 5.49 Billion |
| Market Size 2032 (Forecast Year) | USD 12.43 Billion |
| CAGR | 9.5% |
| Forecast Period | 2024 - 2032 |
| Historical Period | 2018 - 2023 |
LTE Small Base Station Market Insights
According to Market Research Store, the global LTE small base station market size was valued at around USD 5.49 billion in 2023 and is estimated to reach USD 12.43 billion by 2032, to register a CAGR of approximately 9.5% in terms of revenue during the forecast period 2024-2032.
The LTE small base station report provides a comprehensive analysis of the market, including its size, share, growth trends, revenue details, and other crucial information regarding the target market. It also covers the drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges till 2032.
To Get more Insights, Request a Free Sample
Global LTE Small Base Station Market: Overview
An LTE (Long-Term Evolution) small base station is a compact cellular network element designed to provide coverage and improve network performance in a specific, localized area. These small base stations, also known as small cells, are used to complement traditional macro base stations by enhancing data capacity, reducing latency, and improving signal quality in densely populated or hard-to-reach locations. They are commonly deployed in urban environments, office buildings, shopping malls, stadiums, and other venues where traditional macro cells may struggle to provide reliable service.
Key Highlights
- The LTE small base station market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 9.5% during the forecast period.
- The global LTE small base station market was estimated to be worth approximately USD 5.49 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a value of USD 12.43 billion by 2032.
- The growth of the LTE small base station market is being driven by increasing demand for mobile data, the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), and the expansion of 4G and 5G networks.
- Based on the deployment type, the outdoor small base stations segment is growing at a high rate and is projected to dominate the market.
- On the basis of technology, the LTE-FDD (frequency division duplex) segment is projected to swipe the largest market share.
- In terms of size, the pico base stations segment is expected to dominate the market.
- Based on the use case, the urban areas segment is expected to dominate the market.
- In terms of frequency band, the 1-2 GHz segment is expected to dominate the market.
- By region, Asia Pacific is expected to dominate the global market during the forecast period.
LTE Small Base Station Market: Dynamics
Key Growth Drivers:
- Rising Demand for High-Speed Data Connectivity: The increasing demand for high-speed data services, driven by the proliferation of smartphones and IoT devices, is fueling the need for efficient LTE small base stations to provide better coverage and network capacity.
- Growing Adoption of 4G LTE Networks: As telecom operators continue to roll out 4G LTE networks, small base stations are becoming essential to provide efficient coverage, especially in densely populated urban areas.
- Cost Efficiency in Network Expansion: LTE small base stations offer a cost-effective solution for network expansion, particularly in areas where traditional macro base stations would be too expensive or difficult to deploy.
- Increased Mobile Data Traffic: The exponential growth in mobile data consumption due to video streaming, gaming, and social media applications is creating a need for small base stations to offload traffic from macro towers and improve network efficiency.
- Support for Smart City Infrastructure: As cities increasingly adopt smart technologies, LTE small base stations are essential in providing reliable and high-speed connectivity for various IoT devices, sensors, and smart applications.
Restraints:
- High Initial Deployment Costs: While small base stations offer cost savings in operational expenses, the initial cost of deploying them, including installation and integration, can be high, especially for small operators.
- Limited Spectrum Availability: The availability of suitable spectrum for LTE small base stations may be limited in some regions, restricting their deployment and performance.
- Interference and Signal Management Issues: Managing interference between small base stations and ensuring optimal coverage can be challenging, especially in areas with dense deployments.
- Regulatory Challenges: Different countries have varying regulations regarding the deployment of small base stations, which can slow down the adoption of these technologies in certain regions.
Opportunities:
- Adoption of 5G Networks: The transition to 5G networks presents a significant opportunity for LTE small base stations to evolve, as they can serve as a critical part of 5G infrastructure for densification and capacity expansion.
- Rural and Remote Area Coverage: LTE small base stations can be deployed in rural and remote areas where traditional macro base stations may not be economically viable, providing better coverage in underserved regions.
- Integration with Wi-Fi Networks: Small base stations can be integrated with Wi-Fi networks to provide seamless connectivity, especially in indoor environments such as shopping malls, stadiums, and airports.
- Growth in IoT and Connected Devices: With the rise of IoT devices, small base stations will play a crucial role in ensuring reliable connectivity for these devices, opening up new markets in industrial, automotive, and healthcare sectors.
Challenges:
- Network Optimization and Backhaul Connectivity: Ensuring that small base stations are well-integrated into the larger network infrastructure and have reliable backhaul connections can be a significant challenge, especially in areas with limited infrastructure.
- Security and Privacy Concerns: The increased number of small base stations can create potential security vulnerabilities, especially in urban environments where multiple base stations are deployed, raising concerns about data privacy and network security.
- Scalability Issues: As demand for mobile data continues to grow, scaling small base stations to handle increased traffic while maintaining optimal performance can be a technical challenge.
- Complexity in Network Management: Managing a network that includes both macro and small base stations, especially in dense urban environments, can be complex, requiring advanced software solutions and real-time monitoring to ensure optimal performance.
LTE Small Base Station Market: Report Scope
This report thoroughly analyzes the LTE Small Base Station Market, exploring its historical trends, current state, and future projections. The market estimates presented result from a robust research methodology, incorporating primary research, secondary sources, and expert opinions. These estimates are influenced by the prevailing market dynamics as well as key economic, social, and political factors. Furthermore, the report considers the impact of regulations, government expenditures, and advancements in research and development on the market. Both positive and negative shifts are evaluated to ensure a comprehensive and accurate market outlook.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | LTE Small Base Station Market |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 5.49 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2032 | USD 12.43 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 9.5% |
| Number of Pages | 176 |
| Key Companies Covered | Airspan Networks, Alpha Networks Inc, AT&T Intellectual Property, Cisco system Inc., COMMSCOPE Inc., ERICSSON, Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd, Motorola Solutions Inc., Nokia Corporation, ZTE Corporation |
| Segments Covered | By Deployment Type, By Technology, By Size, By Use Case, By Frequency Band, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historical Year | 2018 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2024 to 2032 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
LTE Small Base Station Market: Segmentation Insights
The global LTE small base station market is divided by deployment type, technology, size, use case, frequency band, and region.
Segmentation Insights by Deployment Type
Based on deployment type, the global LTE small base station market is divided into indoor small base stations, outdoor small base stations, and hybrid deployment models.
In the LTE small base station market, the Outdoor Small Base Stations segment is the most dominant. Outdoor small base stations are designed to provide wireless coverage in large outdoor areas, such as urban environments, stadiums, and business districts. They are often deployed to meet high traffic demand and enhance network capacity in locations where traditional cell towers may not be feasible. Their ability to deliver wide coverage with high throughput, particularly in areas with dense populations, makes them highly sought after by network operators.
Following this, the Hybrid Deployment Models segment is growing in importance. Hybrid models combine both indoor and outdoor deployment strategies to offer flexible solutions for network providers. These models help in expanding the coverage of a network and enhancing data speeds by integrating various network architectures. Hybrid deployments are often used in locations that experience high demand, such as airports or shopping malls, where both indoor and outdoor coverage is required. This flexibility makes hybrid models appealing for operators aiming to provide seamless coverage and optimized network performance.
The Indoor Small Base Stations segment, while still significant, ranks third in terms of dominance. Indoor small base stations are typically used in environments such as offices, malls, and homes to provide localized coverage and improve signal strength in areas where outdoor network signals might not reach effectively. Although crucial for maintaining consistent service in small-scale environments, indoor small base stations are limited by their smaller coverage areas compared to outdoor stations, making them less dominant in the overall LTE small base station market.
Segmentation Insights by Technology
On the basis of technology, the global LTE small base station market is bifurcated into LTE-FDD (Frequency Division Duplex), LTE-TDD (Time Division Duplex), LTE-Advanced, and LTE-Advanced Pro.
In the LTE small base station market, the LTE-FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) segment is the most dominant. LTE-FDD is the traditional and widely deployed LTE technology, which uses separate frequencies for uplink and downlink. This method ensures stable and efficient communication, particularly in areas with high user density, making it ideal for many commercial and residential deployments. Its widespread use in networks globally and compatibility with a range of devices, especially in established markets, contributes to its dominant position in the LTE small base station sector.
The LTE-Advanced segment comes next in dominance. LTE-Advanced is an enhancement of the standard LTE technology, offering higher speeds, increased capacity, and improved coverage. It introduces features like carrier aggregation, enhanced MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output), and higher-order modulation schemes to achieve faster data rates and better efficiency. LTE-Advanced is particularly popular in regions that are looking to improve network performance without deploying entirely new infrastructure. Its advanced capabilities make it a crucial technology for operators looking to meet the growing demand for high-speed mobile data.
LTE-TDD (Time Division Duplex) follows as a significant but less dominant segment. LTE-TDD uses the same frequency for both uplink and downlink but divides the time into slots. While it provides efficient spectrum use and is especially effective in areas with asymmetric traffic demands (like high download but low upload), its deployment has been more regional, with higher adoption in certain markets such as China and India. It is less commonly used in developed regions compared to LTE-FDD, which is why its market share is relatively lower, despite its benefits in specific scenarios.
Finally, LTE-Advanced Pro is the least dominant among these technologies. LTE-Advanced Pro builds upon LTE-Advanced and offers even more enhancements, such as greater carrier aggregation (up to 32 carriers), better integration with 5G, and improved network efficiency. It is primarily seen as a stepping stone toward 5G rather than a widespread deployment solution. While it offers significant improvements in speed, efficiency, and user experience, its adoption is still in the early stages compared to the more established LTE-FDD and LTE-Advanced technologies.
Segmentation Insights by Size
Based on size, the global LTE small base station market is divided into micro base stations, pico base stations, and femto base stations.
In the LTE small base station market, Pico Base Stations are the most dominant segment in terms of size. Pico base stations are designed to provide coverage in small to medium-sized areas such as offices, shopping malls, and public spaces, offering a balance between coverage and capacity. These stations are ideal for environments where the user density is moderate, and they support a higher number of simultaneous users compared to micro or femto base stations. Pico base stations are widely used in both urban and suburban areas to improve network capacity and coverage, making them a key component in expanding LTE coverage.
Next in line is the Micro Base Stations segment, which also holds significant importance but ranks slightly behind pico base stations. Micro base stations are typically deployed in medium-sized areas, such as campuses, large offices, or specific outdoor environments, to provide enhanced coverage and capacity. They can support a larger area compared to pico base stations but tend to serve fewer users, making them suitable for places with moderate to high traffic demand. Micro base stations are often deployed to improve the overall network performance in areas with challenging coverage, such as urban environments or dense building structures.
Femto Base Stations are the least dominant segment in terms of size. Femto base stations are primarily designed for home use or very small offices, providing coverage in areas with limited user density. While femto base stations are effective at improving indoor coverage, especially for residential users, they typically support a smaller number of users and are less widely deployed than pico and micro base stations. Femto base stations were initially popular in the early stages of LTE deployment but have become less common as network demand shifted toward solutions that support more users and larger areas.
Segmentation Insights by Use Case
On the basis of use case, the global LTE small base station market is bifurcated into residential, enterprise, public venues, and urban areas.
In the LTE small base station market, the Urban Areas use case is the most dominant. Urban areas have the highest demand for enhanced mobile coverage and capacity due to their dense population, large number of devices, and high traffic volume. Small base stations deployed in urban settings help alleviate network congestion and ensure a consistent, high-quality mobile experience. The need for better coverage in densely populated cities, combined with the growing demand for data services, drives the high adoption of small base stations in these areas. Urban deployments are often focused on providing coverage in both outdoor and indoor environments such as streets, malls, public buildings, and office complexes.
Following urban areas, the Enterprise use case holds significant importance. Enterprises, including businesses, offices, and industrial sites, require small base stations to improve mobile coverage within their premises. As companies rely more heavily on mobile services for communication, collaboration, and data transfer, the demand for high-quality connectivity within office buildings, campuses, and factories has surged. Enterprise deployments of small base stations help improve network performance by addressing coverage gaps, increasing data speeds, and supporting the growing use of connected devices in business environments. Enterprises also use these systems to ensure smooth business operations in areas where traditional cellular infrastructure may not provide adequate coverage.
The Public Venues use case comes next in terms of market share. Public venues such as stadiums, arenas, airports, and shopping malls experience high foot traffic and data usage, creating significant pressure on existing network infrastructure. Small base stations deployed in public venues are essential for enhancing network capacity and providing reliable connectivity to thousands of people simultaneously. These base stations improve the user experience by reducing network congestion and ensuring seamless data transmission during events, travel, and other high-traffic activities.
Finally, the Residential use case, while important, is the least dominant in the LTE small base station market. Residential deployments are primarily focused on improving indoor coverage in homes, particularly in areas with poor cellular signal or in multi-story buildings where traditional network signals may struggle to penetrate. Femto base stations are often used in residential areas to enhance mobile coverage for voice and data services, but with the increasing reliance on Wi-Fi and other home networking technologies, residential small base stations have become less prevalent compared to enterprise, urban, and public venue deployments.
Segmentation Insights by Frequency Band
On the basis of frequency band, the global LTE small base station market is bifurcated into Sub-1 GHz, 1-2 GHz, 2-3 GHz, and above 3 GHz.
In the LTE small base station market, the 1-2 GHz frequency band is the most dominant. This frequency range strikes a balance between coverage and data throughput, making it ideal for a wide range of deployments. Small base stations operating in the 1-2 GHz band can deliver sufficient coverage over medium to large areas while supporting higher data speeds. It is widely used in both urban and suburban settings, providing robust connectivity with relatively lower interference. Additionally, the 1-2 GHz band is widely supported by most devices and is commonly used by network operators, making it a preferred choice for LTE deployments.
The 2-3 GHz frequency band follows as the second most dominant segment. This band provides higher data speeds and lower latency than the 1-2 GHz range, making it ideal for high-traffic areas like stadiums, shopping malls, and business districts. However, its coverage range is more limited compared to the 1-2 GHz band due to the higher frequency's increased signal attenuation, especially in challenging environments like urban canyons or indoor spaces. Despite these challenges, the 2-3 GHz band is preferred in areas with higher demand for capacity and where data speed is the priority.
The Sub-1 GHz frequency band, while important, ranks third in terms of dominance. Sub-1 GHz bands are well-suited for covering larger areas with better penetration, particularly in rural or suburban environments. These lower frequencies allow signals to travel longer distances and penetrate buildings more effectively. As a result, small base stations in this frequency range are often used in rural deployments or to extend coverage in sparsely populated regions. However, they offer lower data speeds and capacity compared to higher-frequency bands, which limits their use in high-density areas where data throughput is more critical.
Finally, the Above 3 GHz frequency band is the least dominant segment. While it supports extremely high data speeds and is suitable for high-capacity environments, such as dense urban areas or venues with large crowds, the coverage is more limited due to the higher frequencies' susceptibility to signal degradation. Additionally, these higher frequencies require more infrastructure for efficient deployment, including more base stations to ensure consistent coverage. As a result, the use of frequencies above 3 GHz is typically reserved for specialized applications or for the next-generation 5G networks, where extremely high data rates and ultra-low latency are essential.
LTE Small Base Station Market: Regional Insights
- Asia Pacific is expected to dominates the global market
Asia Pacific is the most dominant region in the LTE small base station market, driven by rapid urbanization, significant mobile data consumption, and strong government support for digital infrastructure. Countries like China and India are leading the charge, with China focusing on expanding LTE coverage in both urban and rural areas, while India pushes for affordable internet services. The region benefits from a large internet user base and widespread smartphone adoption, fueling the demand for LTE small base stations.
North America ranks second, marked by its advanced telecom infrastructure and high adoption rates of technology. The United States and Canada are investing heavily in upgrading LTE networks to deliver higher data speeds and seamless coverage. The trend of integrating 5G capabilities with LTE is key in this region, helping telecom providers prepare for the next generation of mobile connectivity.
Europe follows closely, with a strong focus on expanding LTE coverage to rural and remote areas to bridge the digital divide. Countries such as Germany, France, and the UK are prioritizing energy-efficient and cost-effective LTE base stations. The growing integration of LTE with 5G technologies is enhancing the capacity of these networks to meet the increasing demand for mobile data.
Latin America is seeing steady growth in the LTE small base station market, driven by network infrastructure investments and government initiatives aimed at reducing the digital divide. Brazil, Argentina, and Chile are the key players in the region, with telecom operators focusing on improving coverage and network capacity to meet the demands of both consumers and businesses.
Middle East and Africa present significant opportunities, particularly due to the large areas of underserved populations and increasing government-led initiatives for digitalization. Countries such as Saudi Arabia, UAE, and South Africa are investing in LTE infrastructure as part of their plans to transition to 5G, enhancing connectivity to foster economic growth.
LTE Small Base Station Market: Competitive Landscape
The report provides an in-depth analysis of companies operating in the LTE small base station market, including their geographic presence, business strategies, product offerings, market share, and recent developments. This analysis helps to understand market competition.
Some of the major players in the global LTE small base station market include:
- Airspan Networks
- Alpha Networks Inc
- AT&T Intellectual Property
- Cisco system Inc.
- COMMSCOPE Inc.
- ERICSSON
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd
- Motorola Solutions Inc.
- Nokia Corporation
- ZTE Corporation
The global LTE small base station market is segmented as follows:
By Deployment Type
- Indoor Small Base Stations
- Outdoor Small Base Stations
- Hybrid Deployment Models
By Technology
- LTE-FDD (Frequency Division Duplex)
- LTE-TDD (Time Division Duplex)
- LTE-Advanced
- LTE-Advanced Pro
By Size
- Micro Base Stations
- Pico Base Stations
- Femto Base Stations
By Use Case
- Residential
- Enterprise
- Public Venues
- Urban Areas
By Frequency Band
- Sub-1 GHz
- 1-2 GHz
- 2-3 GHz
- Above 3 GHz
By Region
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Rest of Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Table Of Content
Inquiry For Buying
LTE Small Base Station
Request Sample
LTE Small Base Station
