Private Blockchain Technology in Energy Market Size, Share, and Trends Analysis Report
CAGR :

| Market Size 2023 (Base Year) | USD 640.49 Million |
| Market Size 2032 (Forecast Year) | USD 2512.41 Million |
| CAGR | 16.4% |
| Forecast Period | 2024 - 2032 |
| Historical Period | 2018 - 2023 |
Private Blockchain Technology in Energy Market Insights
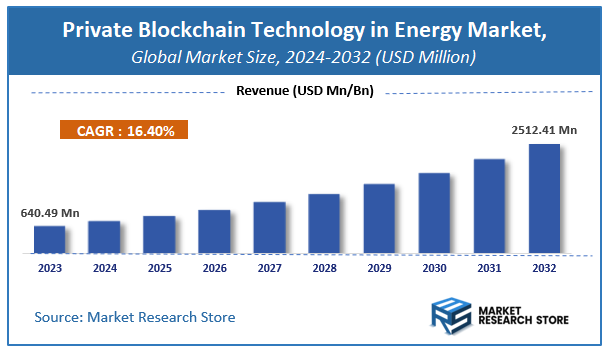
According to Market Research Store, the global private blockchain technology in energy market size was valued at around USD 640.49 million in 2023 and is estimated to reach USD 2512.41 million by 2032, to register a CAGR of approximately 16.4% in terms of revenue during the forecast period 2024-2032.
The private blockchain technology in energy report provides a comprehensive analysis of the market, including its size, share, growth trends, revenue details, and other crucial information regarding the target market. It also covers the drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges till 2032.
To Get more Insights, Request a Free Sample
Private Blockchain Technology in Energy Market: Overview
Private blockchain technology in the energy sector refers to permissioned blockchain networks designed to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency in energy transactions. Unlike public blockchains, private blockchains restrict access to authorized participants, making them ideal for enterprise-level applications such as peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading, grid management, and supply chain tracking. This technology enables decentralized energy distribution, allowing consumers and producers to trade electricity securely without relying on centralized authorities. Additionally, private blockchains streamline operations in renewable energy certification, carbon credit trading, and smart contract automation, improving cost efficiency and reducing fraud risks.
Key Highlights
- The private blockchain technology in energy market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 16.4% during the forecast period.
- The global private blockchain technology in energy market was estimated to be worth approximately USD 640.49 million in 2023 and is projected to reach a value of USD 2512.41 million by 2032.
- The growth of the private blockchain technology in energy market is being driven by increasing demand for decentralized energy solutions, cybersecurity concerns, and regulatory support for digital transformation in the energy sector.
- Based on the component, the platform segment is growing at a high rate and is projected to dominate the market.
- On the basis of technology, the private blockchain segment is projected to swipe the largest market share.
- In terms of deployment model, the on-premises segment is expected to dominate the market.
- Based on the application, the energy trading segment is expected to dominate the market.
- On the basis of end user, the power utilities segment is projected to swipe the largest market share.
- By region, Europe is expected to dominate the global market during the forecast period.
Private Blockchain Technology in Energy Market: Dynamics
Key Growth Drivers
- Enhanced Security & Transparency – Private blockchain ensures tamper-proof transaction records, reducing fraud and increasing trust in energy trading.
- Decentralized Energy Trading – Enables peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading without intermediaries, lowering transaction costs.
- Improved Grid Efficiency – Smart contracts automate and optimize energy distribution, reducing operational inefficiencies.
- Regulatory Push for Renewable Integration – Governments encourage blockchain adoption to manage decentralized renewable energy sources effectively.
Restraints
- High Implementation Cost – Initial setup, infrastructure, and maintenance costs hinder widespread adoption.
- Interoperability Issues – Lack of standardization across blockchain networks limits seamless integration with existing energy systems.
- Scalability Concerns – Handling large volumes of energy transactions in real time remains a technical challenge.
Opportunities
- Growth in Decentralized Energy Systems – Rising adoption of microgrids and distributed energy resources (DERs) creates demand for blockchain solutions.
- Carbon Credit Trading & Sustainability – Blockchain can streamline and authenticate carbon credit transactions, supporting global sustainability goals.
- Advancements in Smart Metering – Secure and automated billing via blockchain enhances accuracy and customer trust.
Challenges
- Regulatory Uncertainty – Lack of clear regulations and compliance frameworks slows blockchain deployment in the energy sector.
- Cybersecurity Risks – Despite strong security, blockchain networks remain vulnerable to cyber threats and hacking.
- Industry Resistance to Change – Traditional energy providers may be reluctant to shift from centralized systems to blockchain-based solutions.
Private Blockchain Technology in Energy Market: Report Scope
This report thoroughly analyzes the Private Blockchain Technology in Energy Market, exploring its historical trends, current state, and future projections. The market estimates presented result from a robust research methodology, incorporating primary research, secondary sources, and expert opinions. These estimates are influenced by the prevailing market dynamics as well as key economic, social, and political factors. Furthermore, the report considers the impact of regulations, government expenditures, and advancements in research and development on the market. Both positive and negative shifts are evaluated to ensure a comprehensive and accurate market outlook.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Private Blockchain Technology in Energy Market |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 640.49 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2032 | USD 2512.41 Million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 16.4% |
| Number of Pages | 190 |
| Key Companies Covered | IBM, Microsoft, Accenture, ConsenSys, Infosys, Drift, Electron, Btl Group Ltd., LO3 Energy Inc, Power Ledger |
| Segments Covered | By Component, By Technology, By Deployment Model, By Application, By End User, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year |
2023 |
| Historical Year | 2018 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2024 to 2032 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Private Blockchain Technology in Energy Market: Segmentation Insights
The global private blockchain technology in energy market is divided by component, technology, deployment model, application, end user, and region.
Segmentation Insights by Component
Based on component, the global private blockchain technology in energy market is divided into platform and services.
The Platform segment holds the most dominant position in the private blockchain technology in energy market. This segment primarily includes blockchain frameworks and software solutions that enable energy companies to implement decentralized, secure, and transparent transactions. Energy providers, grid operators, and renewable energy firms are increasingly adopting blockchain platforms to optimize energy trading, manage distributed energy resources, and enhance grid security. The growing demand for peer-to-peer energy trading and smart contracts further propels the adoption of blockchain platforms, making them the most sought-after component in this market. Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence and IoT with blockchain platforms enhances efficiency, driving their dominance.
The Services segment, while important, holds a comparatively smaller market share. This segment encompasses consulting, integration, and maintenance services that support the implementation and operation of blockchain platforms. Companies require specialized services to ensure seamless deployment, scalability, and regulatory compliance of blockchain-based energy solutions. The demand for consulting services is rising as energy firms seek guidance on implementing blockchain in their operations. However, the reliance on third-party service providers and the growing internal expertise of energy firms in blockchain technology slightly limit the dominance of this segment compared to the platform segment.
Segmentation Insights by Technology
On the basis of technology, the global private blockchain technology in energy market is bifurcated into private blockchain, consortium blockchain, and hybrid blockchain.
The Private Blockchain segment is the most dominant in the private blockchain technology in the energy market. Energy companies prefer private blockchains due to their controlled access, enhanced security, and ability to comply with industry regulations. These blockchains are widely used for internal operations, such as managing energy transactions, optimizing supply chains, and ensuring transparency in renewable energy credits. Utilities and grid operators particularly favor private blockchains for their ability to prevent unauthorized access and maintain data privacy while enabling seamless automation through smart contracts. The rising need for secure and efficient energy trading solutions further strengthens the dominance of this segment.
The Consortium Blockchain segment follows as the second most significant, as multiple stakeholders within the energy sector increasingly collaborate on shared blockchain networks. Consortium blockchains allow controlled access while enabling cooperation among energy producers, suppliers, and regulators. They are particularly beneficial for projects that require a balance of decentralization and governance, such as peer-to-peer energy trading platforms and decentralized grid management. The need for industry-wide standardization and collaborative energy trading initiatives has driven the adoption of consortium blockchains, though their complexity in governance and decision-making slightly limits their growth compared to private blockchains.
The Hybrid Blockchain segment, while gaining traction, remains the least dominant. This technology combines elements of both private and public blockchains, offering flexibility in data accessibility and security. Hybrid blockchains are particularly useful in scenarios where some data needs to be publicly verifiable (such as carbon credit transactions), while other data must remain confidential. However, their adoption in the energy market is still in the early stages, primarily due to challenges in implementation, interoperability, and regulatory concerns. As the energy sector continues to explore innovative blockchain applications, hybrid blockchains may see increased adoption in the future.
Segmentation Insights by Deployment Model
On the basis of deployment model, the global private blockchain technology in energy market is bifurcated into on-premises and cloud.
The On-Premises deployment model holds the dominant position in the private blockchain technology in the energy market. Energy companies, especially large-scale utilities and grid operators, prefer on-premises blockchain solutions due to their high security, complete control over data, and compliance with strict industry regulations. Since energy transactions and supply chain management involve sensitive data, companies prioritize on-premises deployments to mitigate cybersecurity risks and prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, on-premises solutions provide better customization options, allowing energy firms to tailor blockchain applications to their specific operational needs. However, the high initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs pose challenges for smaller players in the industry.
The Cloud deployment model, while growing, is comparatively less dominant. Cloud-based blockchain solutions offer scalability, cost-effectiveness, and remote accessibility, making them an attractive option for startups and mid-sized energy firms. The ability to integrate blockchain with other cloud-based technologies, such as IoT and AI, enhances operational efficiency and simplifies data management. However, concerns over data privacy, regulatory compliance, and dependency on third-party cloud providers limit the widespread adoption of cloud-based blockchain solutions in the energy sector. Despite these challenges, the increasing shift toward digital transformation and advancements in cloud security are expected to drive the growth of this segment in the coming years.
Segmentation Insights by Application
On the basis of application, the global private blockchain technology in energy market is bifurcated into energy trading, grid management, peer-to-peer energy transactions, supply chain management, and smart contracts.
The Energy Trading segment is the most dominant application in the private blockchain technology in the energy market. The adoption of blockchain in energy trading is driven by the need for secure, transparent, and efficient transactions between producers, suppliers, and consumers. Private blockchain technology enables real-time settlements, reduces transaction costs, and eliminates intermediaries, making energy trading more efficient and profitable. Large energy corporations and independent power producers are increasingly leveraging blockchain-based platforms to facilitate cross-border energy trades and manage price volatility. The rising demand for decentralized and automated energy trading solutions continues to fuel the dominance of this segment.
The Grid Management segment follows as the second most significant application. With the growing complexity of power grids and the integration of renewable energy sources, energy providers use blockchain to enhance grid stability, track energy flows, and optimize distribution networks. Blockchain enables automated and transparent grid management, reducing inefficiencies and improving response times in case of power fluctuations. The integration of IoT with blockchain further enhances real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, making it a key technology for smart grid development.
The Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Energy Transactions segment is gaining significant traction, as blockchain enables direct energy trading between consumers, prosumers, and microgrid participants. With the rise of distributed energy resources such as solar panels, blockchain facilitates transparent and automated energy exchanges without the need for a central authority. Consumers can sell excess energy directly to other users, fostering decentralized energy markets. However, regulatory challenges and infrastructure limitations slightly hinder the widespread adoption of P2P energy trading at present.
The Supply Chain Management segment plays a crucial role in tracking and verifying the authenticity of energy sources. Blockchain enhances transparency in the energy supply chain by securely recording data on fuel sourcing, transportation, and storage. It is particularly useful for ensuring compliance with sustainability regulations and verifying the origin of renewable energy certificates. As the energy sector moves towards cleaner and more traceable supply chains, blockchain adoption in this area is expected to grow further.
The Smart Contracts segment, while important, currently holds the smallest market share. Smart contracts automate and enforce energy agreements, reducing the need for manual paperwork and intermediaries. They are widely used in power purchase agreements, billing automation, and demand response programs. However, the complexity of integrating smart contracts with legacy energy systems and regulatory uncertainties slow down their widespread implementation. As blockchain adoption matures, smart contracts are expected to play a more significant role in streamlining energy sector transactions.
Segmentation Insights by End User
On the basis of end user, the global private blockchain technology in energy market is bifurcated into power utilities, oil & gas companies, renewable energy providers, energy retailers, and consumers.
The Power Utilities segment holds the most dominant position in the private blockchain technology in energy market. Power utilities leverage blockchain to enhance grid management, energy trading, and supply chain operations. With the increasing integration of renewable energy sources and smart grids, utilities use blockchain to track energy distribution, optimize demand-response systems, and improve overall operational efficiency. The ability of blockchain to provide secure, transparent, and automated transactions makes it a critical tool for large-scale energy providers. Additionally, regulatory compliance and data security concerns drive utilities to adopt private blockchain solutions over public alternatives.
The Oil & Gas Companies segment follows as the second most significant end-user group. These companies utilize blockchain for supply chain transparency, fraud prevention, and contract automation. Blockchain enhances operational efficiency by tracking crude oil and gas shipments, managing pipeline transactions, and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. The ability to reduce paperwork and improve transaction speed in oil and gas trading further drives its adoption. However, compared to power utilities, the use of blockchain in oil & gas is still evolving, with companies gradually integrating it into their operations.
The Renewable Energy Providers segment is rapidly gaining traction as decentralized energy generation grows. Blockchain facilitates peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing renewable energy producers to sell excess electricity directly to consumers without intermediaries. It also plays a crucial role in verifying renewable energy certificates (RECs) and tracking carbon credits, ensuring transparency in the sustainability market. As the global push for clean energy intensifies, blockchain adoption among renewable energy providers is expected to accelerate.
The Energy Retailers segment benefits from blockchain by streamlining billing processes, reducing transaction costs, and enhancing customer engagement. Energy retailers use blockchain to offer dynamic pricing models, track energy consumption, and provide secure payment options. The ability to integrate blockchain with smart meters and IoT devices allows retailers to create more flexible and consumer-friendly energy plans. However, regulatory constraints and legacy system integration challenges limit the widespread use of blockchain in this segment.
The Consumers segment, while the least dominant, is steadily growing with the rise of decentralized energy markets. Residential and commercial energy consumers are increasingly adopting blockchain-powered platforms for peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading, real-time energy tracking, and automated billing. Consumers with solar panels and battery storage systems benefit the most, as blockchain allows them to trade excess energy seamlessly. However, awareness and regulatory barriers remain key challenges for large-scale consumer adoption. As blockchain technology matures and regulatory frameworks evolve, consumer participation in blockchain-enabled energy transactions is expected to rise.
Private Blockchain Technology in Energy Market: Regional Insights
- Europe is expected to dominates the global market
Europe dominates the private blockchain technology in energy market, driven by its leadership in renewable energy adoption and smart grid innovations. The region actively integrates blockchain for peer-to-peer energy trading, grid optimization, and cross-border electricity transactions. Germany leads this transformation with a strong focus on decentralized energy solutions and digitalization of energy infrastructure. Collaborative projects between energy providers and blockchain firms accelerate the deployment of transparent and efficient energy management systems. Regulatory support and investments in digital energy solutions further solidify Europe's dominance in this sector.
North America follows closely, with the United States being a major contributor to blockchain advancements in the energy industry. The region prioritizes decentralized energy systems, particularly in renewable energy trading and grid modernization. Leading energy firms and startups drive innovation through blockchain applications in demand response management and carbon credit tracking. Government-backed initiatives and investments in modernizing the electricity grid strengthen the region's position as a key player in blockchain-powered energy solutions.
Asia-Pacific is rapidly expanding its adoption of private blockchain technology in the energy market, spurred by urbanization and growing electricity demands. China, Japan, and India spearhead blockchain-driven energy projects, leveraging the technology for distributed energy resource management, smart city development, and real-time energy trading. Blockchain integration with IoT and AI in energy distribution networks enhances grid efficiency and reduces operational costs. The region’s emphasis on technological advancements and sustainability accelerates its progress in this sector.
Middle East & Africa is gradually incorporating blockchain technology into its energy systems, primarily focusing on renewable energy integration and supply chain transparency. The United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia lead the efforts with blockchain-supported solar energy trading platforms and digital energy management initiatives. Governments in the region are leveraging blockchain to enhance energy security, optimize resource allocation, and support large-scale sustainable energy projects. These developments align with the region’s long-term vision of energy diversification and efficiency.
Latin America is in the early stages of blockchain adoption in the energy sector, with efforts concentrated on enhancing transparency in energy transactions and improving infrastructure efficiency. Countries such as Brazil and Chile are exploring blockchain-based solutions for renewable energy certification and decentralized electricity trading. While adoption is still developing, increasing interest in digital transformation and sustainable energy practices indicates potential growth for blockchain integration in the region’s energy market.
Private Blockchain Technology in Energy Market: Competitive Landscape
The report provides an in-depth analysis of companies operating in the private blockchain technology in energy market, including their geographic presence, business strategies, product offerings, market share, and recent developments. This analysis helps to understand market competition.
Some of the major players in the global private blockchain technology in energy market include:
- IBM
- Microsoft
- Accenture
- ConsenSys
- Infosys
- Drift
- Electron
- Btl Group Ltd.
- LO3 Energy Inc
- Power Ledger
The global private blockchain technology in energy market is segmented as follows:
By Component
- Platform
- Services
By Technology
- Private Blockchain
- Consortium Blockchain
- Hybrid Blockchain
By Deployment Model
- On-Premises
- Cloud
By Application
- Energy Trading
- Grid Management
- Peer-to-Peer Energy Transactions
- Supply Chain Management
- Smart Contracts
By End User
- Power Utilities
- Oil and Gas Companies
- Renewable Energy Providers
- Energy Retailers
- Consumers
By Region
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Rest of Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Table Of Content
Inquiry For Buying
Private Blockchain Technology in Energy
Request Sample
Private Blockchain Technology in Energy
