Wearables and Workforce Automation Market Size, Share, and Trends Analysis Report
CAGR :

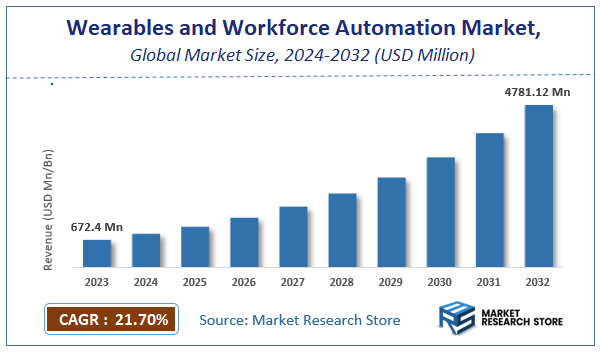
| Market Size 2023 (Base Year) | USD 672.4 Million |
| Market Size 2032 (Forecast Year) | USD 4781.12 Million |
| CAGR | 21.7% |
| Forecast Period | 2024 - 2032 |
| Historical Period | 2018 - 2023 |
Wearables and Workforce Automation Market Insights
According to Market Research Store, the global wearables and workforce automation market size was valued at around USD 672.4 million in 2023 and is estimated to reach USD 4781.12 million by 2032, to register a CAGR of approximately 21.7% in terms of revenue during the forecast period 2024-2032.
The wearables and workforce automation report provides a comprehensive analysis of the market, including its size, share, growth trends, revenue details, and other crucial information regarding the target market. It also covers the drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges till 2032.
To Get more Insights, Request a Free Sample
Global Wearables and Workforce Automation Market: Overview
Wearables and workforce automation refer to the integration of wearable technology with automated systems to enhance operational efficiency, safety, and productivity in various industries. Wearable devices such as smartwatches, smart glasses, fitness bands, and exoskeletons are used to collect real-time data, monitor worker health and performance, and facilitate hands-free access to critical information. Workforce automation involves the use of AI, machine learning, robotics, and software solutions to automate repetitive or dangerous tasks, streamline workflows, and improve decision-making. Together, wearables and automation form a connected ecosystem that transforms the way businesses manage their human resources, especially in sectors like manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and construction.
Key Highlights
- The wearables and workforce automation market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 21.7% during the forecast period.
- The global wearables and workforce automation market was estimated to be worth approximately USD 672.4 million in 2023 and is projected to reach a value of USD 4781.12 million by 2032.
- The growth of the wearables and workforce automation market is being driven by increasing demand for operational efficiency, employee safety, and data-driven insights across various industries.
- Based on the product type, the smartwatches segment is growing at a high rate and is projected to dominate the market.
- On the basis of application, the healthcare segment is projected to swipe the largest market share.
- In terms of technology, the Internet of Things (IoT) segment is expected to dominate the market.
- Based on the end-user, the healthcare segment is expected to dominate the market.
- By region, North America is expected to dominate the global market during the forecast period.
Wearables and Workforce Automation Market: Dynamics
Key Growth Drivers
- Operational Efficiency Demands: Rising need to optimize productivity and reduce operational costs through real-time data from wearables (e.g., smart glasses, IoT sensors) and automated workflows.
- Labor Shortages: Automation of repetitive tasks (e.g., inventory management, assembly lines) to address workforce gaps, particularly in manufacturing and logistics.
- Worker Safety Compliance: Wearables (e.g., fatigue-monitoring headsets, environmental sensors) enhance workplace safety and adherence to OSHA and other regulations.
- AI and IoT Integration: Advanced analytics and machine learning enable predictive maintenance, task prioritization, and personalized worker insights.
Restraints
- High Implementation Costs: Expenses for hardware, software integration, and employee training limit adoption, especially for SMEs.
- Privacy Concerns: Resistance from workers over data collection (e.g., biometric tracking, location monitoring) and potential misuse.
- Technical Limitations: Battery life, device durability, and connectivity issues in harsh industrial environments.
- Cultural Resistance: Skepticism among employees about surveillance and job displacement fears due to automation.
Opportunities
- Healthcare and Remote Monitoring: Expansion into healthcare for patient care automation and wearable health trackers in hazardous workplaces.
- Edge Computing Adoption: Faster data processing via edge devices to reduce latency in automated decision-making.
- Customized Solutions: Industry-specific wearables (e.g., exoskeletons for construction, AR glasses for field technicians) to address niche needs.
- Emerging Markets: Growth in Asia-Pacific and Latin America due to industrialization and smart factory initiatives.
Challenges
- Interoperability Issues: Fragmented ecosystems of devices, software, and legacy systems hinder seamless integration.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating diverse global standards for data privacy, worker safety, and device certifications.
- Skill Gaps: Shortage of workers trained to operate and maintain advanced automation tools and wearable tech.
- Sustainability Pressures: Balancing energy consumption of automated systems and e-waste from obsolete wearables.
Wearables and Workforce Automation Market: Report Scope
This report thoroughly analyzes the Wearables and Workforce Automation Market, exploring its historical trends, current state, and future projections. The market estimates presented result from a robust research methodology, incorporating primary research, secondary sources, and expert opinions. These estimates are influenced by the prevailing market dynamics as well as key economic, social, and political factors. Furthermore, the report considers the impact of regulations, government expenditures, and advancements in research and development on the market. Both positive and negative shifts are evaluated to ensure a comprehensive and accurate market outlook.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Wearables and Workforce Automation Market |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 672.4 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2032 | USD 4781.12 Million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 21.7% |
| Number of Pages | 170 |
| Key Companies Covered | Accenture, Augmate, Capgemini, Invata, Iomart, PTC, Salesforce, SOTI, SpiderCloud Wireless, Upskill, VMware, Zerintia |
| Segments Covered | By Product Type, By Application, By Technology, By End-User, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historical Year | 2018 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2024 to 2032 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Wearables and Workforce Automation Market: Segmentation Insights
The global wearables and workforce automation market is divided by product type, application, technology, end-user, and region.
Segmentation Insights by Product Type
Based on product type, the global wearables and workforce automation market is divided into smartwatches, fitness trackers, smart glasses, wearable cameras, and others.
In the wearables and workforce automation market, smartwatches emerge as the most dominant product segment. Their dominance is attributed to their multifunctionality, including timekeeping, health monitoring, task scheduling, and communication capabilities. Smartwatches are widely adopted across industries like logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing due to their ability to streamline workflows, enable real-time communication, and monitor worker productivity and well-being. Integration with workforce management software and compatibility with various enterprise platforms further enhance their appeal in corporate and industrial environments.
Following smartwatches, fitness trackers hold a strong position, particularly in physically intensive work environments. These devices focus on health metrics like heart rate, movement, sleep patterns, and energy levels, which are crucial for workforce wellness initiatives. Many organizations implement fitness trackers to promote healthier lifestyles, reduce absenteeism, and improve employee performance, especially in sectors such as construction, warehousing, and field services.
Smart glasses come next, gaining traction primarily in sectors requiring hands-free operations, such as manufacturing, logistics, and field maintenance. These devices allow workers to access manuals, instructions, or real-time video support while keeping their hands free for tasks. Augmented reality (AR) features in smart glasses improve efficiency in complex procedures like remote troubleshooting, quality inspections, and assembly line management.
Wearable cameras are less dominant but hold significant value in industries where documentation, safety monitoring, or remote communication is critical. These are used in law enforcement, field service, and security sectors to record interactions, monitor compliance, and provide real-time video feeds. Their adoption is increasing, but limitations around privacy concerns and data management slightly hinder their widespread integration.
Segmentation Insights by Application
On the basis of application, the global wearables and workforce automation market is bifurcated into healthcare, manufacturing, retail, logistics, and others.
In the wearables and workforce automation market by application, the healthcare sector stands out as the most dominant segment. The adoption of wearable technology in healthcare is driven by the increasing demand for real-time patient monitoring, health tracking, and hands-free communication among medical staff. Devices such as smartwatches and fitness trackers are extensively used for monitoring vital signs, managing chronic conditions, and improving response times in emergency care. Furthermore, wearable technology aids in remote patient care, telemedicine, and hospital workflow management, making it indispensable in modern healthcare environments.
Manufacturing follows as the next most prominent application area. Wearables in manufacturing improve operational efficiency and worker safety. Devices like smart glasses and wearable sensors enable real-time access to data, instructions, and remote support, which is especially useful in complex assembly lines and equipment maintenance. Additionally, wearable technologies enhance safety by monitoring fatigue levels, posture, and exposure to hazardous conditions. These functionalities contribute to reduced downtime, better compliance, and lower injury rates in industrial settings.
The retail industry is increasingly leveraging wearable devices to enhance customer service and streamline workforce operations. Wearables like smartwatches and wearable communication devices allow store associates to receive real-time inventory updates, customer service notifications, and task assignments, enabling faster response times and better in-store experience. In warehouse retail environments, wearable scanners and AR-enabled glasses help in inventory picking and replenishment processes, improving overall supply chain efficiency.
Logistics is another key application area, where wearables support route optimization, delivery tracking, and warehouse management. Workers benefit from hands-free devices such as smart glasses and wearable barcode scanners that facilitate quicker and more accurate sorting, picking, and shipping processes. Real-time tracking of employee location and performance also enhances accountability and resource allocation in supply chain operations, although adoption here is slightly behind healthcare and manufacturing due to infrastructure challenges and cost concerns.
Segmentation Insights by Technology
Based on technology, the global wearables and workforce automation market is divided into IoT, AI, AR/VR, and others.
In the wearables and workforce automation market by technology, Internet of Things (IoT) leads as the most dominant segment. IoT serves as the backbone of wearable functionality by enabling real-time data collection, communication, and integration across connected devices. In workforce environments, IoT allows smartwatches, fitness trackers, and other wearables to continuously monitor vital metrics like location, activity levels, temperature, and health data. This real-time feedback is crucial in sectors like healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing for improving efficiency, enhancing safety, and enabling predictive maintenance. The scalability and adaptability of IoT solutions contribute significantly to its dominance in the market.
Next in line is Artificial Intelligence (AI), which plays a critical role in making wearable data actionable. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data gathered from wearable devices to derive insights related to worker performance, health risks, fatigue detection, and workflow optimization. In healthcare, AI enhances diagnostic accuracy and patient monitoring, while in industrial settings, it supports decision-making, automation, and anomaly detection. Though slightly behind IoT in terms of adoption, AI’s growing integration into wearables is rapidly transforming how organizations leverage workforce intelligence.
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality (AR/VR) technology, while less dominant than IoT and AI, holds a unique and rapidly expanding role in workforce automation—particularly in training, maintenance, and remote collaboration. AR-powered smart glasses are used for step-by-step visual instructions, real-time support, and remote troubleshooting in manufacturing and logistics. VR, meanwhile, is gaining traction for immersive training simulations, especially in high-risk industries like construction and aviation. However, the high cost of deployment, hardware limitations, and the need for specialized applications currently limit the broader adoption of AR/VR, positioning it as the least dominant—yet highly promising—segment in this technology category.
Segmentation Insights by End-User
On the basis of end-user, the global wearables and workforce automation market is bifurcated into BFSI, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, IT & telecommunications, and others.
In the wearables and workforce automation market by end-user, healthcare is the most dominant sector. This leadership stems from the critical need for real-time health monitoring, improved communication among medical staff, and enhanced patient care. Wearables such as smartwatches and fitness trackers are widely used for tracking vital signs, monitoring chronic conditions, and alerting healthcare workers to emergencies. Additionally, wearables help streamline hospital workflows, manage staff schedules, and improve overall operational efficiency. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated wearable adoption in this sector for remote patient monitoring and telehealth applications.
Manufacturing follows closely behind as another major end-user. Wearables in manufacturing help boost productivity, ensure worker safety, and enable hands-free access to operational data. Smart glasses are commonly used for step-by-step instructions, quality checks, and remote assistance, while wearable sensors track workers' posture, fatigue, and exposure to hazardous environments. These devices reduce errors and downtime, making them invaluable in complex industrial processes and hazardous work conditions.
The retail sector is increasingly adopting wearables to enhance in-store operations and improve customer service. Employees use smartwatches and wearable communication devices to receive task notifications, inventory updates, and customer requests in real time. In warehouse-style retail environments, wearables support inventory picking and order fulfillment with speed and accuracy. While not as mature as healthcare or manufacturing, the retail sector’s growing focus on automation and customer experience is fueling wearable adoption.
Information Technology (IT) & Telecommunications is an emerging end-user segment where wearables are used primarily for productivity tracking, workforce management, and health monitoring in tech-heavy environments. In software development and tech support teams, wearables assist with time tracking, meeting coordination, and wellness programs. However, adoption is more organizational and health-centric rather than operational, placing this sector slightly behind retail in terms of market dominance.
Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) uses wearables mostly for employee wellness programs and to some extent for identity verification and access control. Though the BFSI sector is highly digitized, the use of wearables for core operational functions remains limited. The focus is more on employee engagement and security, resulting in lower adoption rates compared to more operationally intensive industries.
Wearables and Workforce Automation Market: Regional Insights
- North America is expected to dominates the global market
The North America region is the most dominant in the wearables and workforce automation market. Its leadership is driven by high levels of technological innovation, widespread enterprise digital transformation, and early adoption of workforce automation tools. The strong presence of major tech companies, coupled with a robust industrial sector, accelerates the implementation of smart wearables for safety, productivity tracking, and hands-free operations. The U.S. leads in deploying AI-powered wearable devices across logistics, manufacturing, and healthcare sectors.
The Asia Pacific region follows closely, fueled by the expansion of industrial and manufacturing activities in countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India. Rapid digitalization and government initiatives to modernize labor-intensive sectors have contributed to widespread adoption of wearables for monitoring worker performance, safety compliance, and health metrics. Local tech firms and OEMs are also innovating cost-effective devices tailored for the regional workforce, driving further market penetration.
The Europe region holds a significant position, supported by strict occupational safety regulations and a high focus on automation in manufacturing. Countries such as Germany, the UK, and France are investing in smart factory concepts where wearables play a key role in optimizing human-machine collaboration and operational efficiency. European industries are especially keen on data analytics integration with wearable tech for predictive maintenance and workforce management.
In Latin America, the market is gradually gaining momentum, especially in countries like Brazil and Mexico. The demand is rising as industries in the region aim to enhance productivity and workplace safety through automation. Wearables such as smart helmets and AR glasses are being introduced for training and maintenance tasks in construction and utilities, although cost sensitivity remains a challenge to mass adoption.
The Middle East and Africa region is the least dominant but shows promising growth potential. With increasing investment in smart infrastructure, oil & gas, and logistics sectors, there is growing interest in workforce wearables to enhance field worker safety and task efficiency. While adoption is still in its early stages, pilot programs and partnerships with international tech firms are helping build momentum in key urban centers.
Wearables and Workforce Automation Market: Competitive Landscape
The report provides an in-depth analysis of companies operating in the wearables and workforce automation market, including their geographic presence, business strategies, product offerings, market share, and recent developments. This analysis helps to understand market competition.
Some of the major players in the global wearables and workforce automation market include:
- Accenture
- Augmate
- Capgemini
- Invata
- Iomart
- PTC
- Salesforce
- SOTI
- SpiderCloud Wireless
- Upskill
- VMware
- Zerintia
The global wearables and workforce automation market is segmented as follows:
By Product Type
- Smartwatches
- Fitness Trackers
- Smart Glasses
- Wearable Cameras
- Others
By Application
- Healthcare
- Manufacturing
- Retail
- Logistics
- Others
By Technology
- IoT
- AI
- AR/VR
- Others
By End-User
- BFSI
- Healthcare
- Retail
- Manufacturing
- IT and Telecommunications
- Others
By Region
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Rest of Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Table Of Content
Inquiry For Buying
Wearables and Workforce Automation
Request Sample
Wearables and Workforce Automation
