Low-Code Development Platform Market Size, Share, and Trends Analysis Report
CAGR :

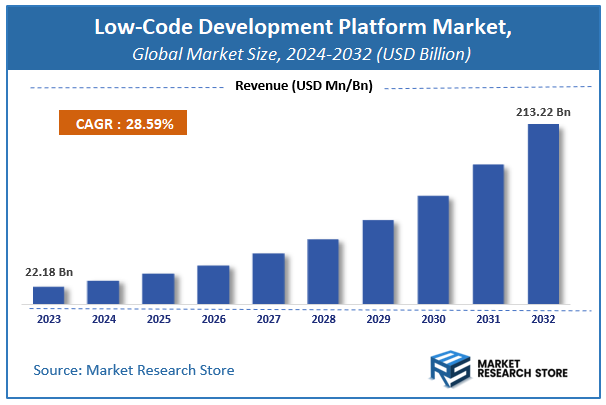
| Market Size 2023 (Base Year) | USD 22.18 Billion |
| Market Size 2032 (Forecast Year) | USD 213.22 Billion |
| CAGR | 28.59% |
| Forecast Period | 2024 - 2032 |
| Historical Period | 2018 - 2023 |
Low-Code Development Platform Market Insights
According to Market Research Store, the global low-code development platform market size was valued at around USD 22.18 billion in 2023 and is estimated to reach USD 213.22 billion by 2032, to register a CAGR of approximately 28.59% in terms of revenue during the forecast period 2024-2032.
The low-code development platform report provides a comprehensive analysis of the market, including its size, share, growth trends, revenue details, and other crucial information regarding the target market. It also covers the drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges till 2032.
Global Low-Code Development Platform Market: Overview
A low-code development platform is a software environment that enables users to create applications with minimal hand-coding, using graphical user interfaces, drag-and-drop tools, and prebuilt templates. These platforms simplify and accelerate the software development process by abstracting complex coding tasks and offering reusable components for workflows, forms, APIs, databases, and UI design. Low-code platforms are widely used for developing web and mobile apps, internal business tools, and process automation solutions. They support rapid prototyping, iterative development, and deployment with minimal technical expertise, making them accessible to both professional developers and business users (often referred to as citizen developers).
The growth of low-code development platforms is driven by increasing demand for faster application delivery, rising digital transformation initiatives, and a shortage of skilled software developers. Organizations are turning to low-code solutions to bridge IT backlogs, enhance agility, and empower non-technical teams to build functional applications without compromising governance or scalability. Integration capabilities with legacy systems, cloud services, and third-party applications further expand their utility across industries. As enterprises seek to respond swiftly to changing market needs and automate business operations, low-code platforms are emerging as critical tools for democratizing app development and accelerating innovation.
Key Highlights
- The low-code development platform market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 28.59% during the forecast period.
- The global low-code development platform market was estimated to be worth approximately USD 22.18 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a value of USD 213.22 billion by 2032.
- The growth of the low-code development platform market is being driven by the accelerated pace of digital transformation across all industries.
- Based on the application type, the web-based segment is growing at a high rate and is projected to dominate the market.
- On the basis of deployment type, the cloud segment is projected to swipe the largest market share.
- In terms of organization size, the SME segment is expected to dominate the market.
- Based on the end-use, the BFSI segment is expected to dominate the market.
- By region, North America is expected to dominate the global market during the forecast period.
Low-Code Development Platform Market: Dynamics
Key Growth Drivers:
- Accelerated Digital Transformation Initiatives: Businesses across all industries are undergoing rapid digital transformation to enhance operations, improve customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge. Low-code platforms enable organizations to develop and deploy applications much faster than traditional methods, significantly accelerating these digital initiatives.
- Growing Demand for Rapid Application Development (RAD): The fast-paced business environment necessitates quick responses to market changes and evolving customer needs. Low-code platforms drastically reduce development time (by 50-90% according to some reports), allowing companies to build and iterate applications in days or weeks instead of months.
- Addressing the Developer Shortage and IT Backlog: There's a persistent global shortage of skilled software developers, leading to significant IT backlogs and delays in bringing new applications to market. Low-code platforms empower citizen developers and even junior professional developers to create applications, bridging the talent gap and alleviating the burden on IT departments.
- Emphasis on Business Agility and Innovation: Low-code platforms enable businesses to quickly adapt to new opportunities and challenges by providing the flexibility to develop, test, and deploy applications rapidly. This fosters a culture of continuous innovation and allows organizations to experiment with new ideas more easily.
- Democratization of Application Development ("Citizen Development"): Low-code platforms simplify the development process, making it accessible to non-technical business users. This "citizen development" movement empowers employees outside of traditional IT to build solutions for their specific departmental needs, increasing overall organizational efficiency and reducing reliance on central IT.
- Cost Reduction in Application Development: By streamlining development processes, reducing the need for extensive coding, and enabling faster time-to-market, low-code platforms significantly cut down on development costs, including labor expenses and infrastructure investments.
- Integration of AI and Machine Learning Capabilities: The incorporation of AI and ML into low-code platforms enhances their functionality, allowing for intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and even AI-assisted code generation. This makes complex AI functionalities accessible to a broader range of users without deep coding knowledge.
- Shift to Cloud-Based Deployment: The prevalence of cloud computing offers inherent flexibility, scalability, and reduced maintenance for low-code platforms. Cloud-based low-code solutions are gaining traction due to their accessibility, automatic updates, and ability to support remote collaboration.
Restraints:
- Limited Customization and Flexibility: While low-code excels at rapid development, it can sometimes offer limited customization options compared to traditional hand-coding. Highly unique or complex business requirements that deviate significantly from pre-built templates or components might be challenging to implement, potentially leading to a "lowest common denominator" application.
- Integration Complexity with Legacy Systems: Integrating low-code applications with existing legacy systems, complex databases, or highly specialized third-party software can be challenging. While many platforms offer connectors, deep, bidirectional integration often requires significant effort or custom coding.
- Vendor Lock-in Concerns: Investing heavily in a specific low-code platform can lead to vendor lock-in, making it difficult and costly to switch to another platform later if business needs change or the vendor's offerings no longer align. This can restrict long-term flexibility and control.
- Scalability Limitations for Enterprise-Grade Applications: While low-code platforms are becoming more robust, concerns about their ability to scale to handle extremely high transaction volumes, complex data processing, or mission-critical enterprise applications persist for some organizations.
- Security and Governance Risks ("Shadow IT"): The ease of use of low-code can lead to "shadow IT" – applications built by business users without proper IT oversight. This can introduce security vulnerabilities, data integrity issues, compliance risks, and governance challenges if not managed effectively by central IT.
- Performance Issues and Code Bloat: Visually built applications might sometimes generate less optimized code compared to expertly hand-coded applications, potentially leading to performance bottlenecks, larger file sizes, or inefficient resource utilization.
- Dependence on Platform Features and Updates: The functionality of a low-code application is largely dependent on the features and updates provided by the platform vendor. If a required feature isn't supported or updates are slow, it can hinder development or force workarounds.
Opportunities:
- Hyper-Automation and Workflow Orchestration: Low-code platforms are pivotal in driving hyper-automation by enabling rapid development of applications that streamline and automate complex business workflows, approvals, and data handling across various systems. This is a massive area for growth.
- AI-Powered Low-Code Tools: The continued integration of advanced AI capabilities, such as natural language processing (NLP) for building conversational interfaces, AI-driven code suggestions, intelligent automation of testing, and predictive analytics, will further enhance the power and reach of low-code platforms.
- Industry-Specific Low-Code Solutions: Developing highly specialized low-code platforms or templates tailored to the unique needs and regulatory requirements of specific industries (e.g., healthcare, BFSI, manufacturing, supply chain) presents a significant opportunity for niche market penetration and value creation.
- Composable Architectures and Microservices Integration: Low-code platforms that seamlessly integrate with composable architectures, microservices, and API-driven ecosystems allow organizations to assemble modular applications, promoting reusability and greater flexibility in enterprise IT.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Application Development: As AR/VR technologies mature, low-code platforms can provide a simplified way for developers and designers to create immersive applications without extensive 3D modeling or complex coding, opening up new application domains.
- Expansion into Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs): The affordability and ease of use of low-code platforms make them highly attractive to SMEs, which often have limited IT resources and budgets. This segment represents a vast, largely untapped market for low-code adoption.
- Citizen Developer Programs and Governance Frameworks: As more organizations embrace citizen development, there's an opportunity for vendors to offer comprehensive governance frameworks, training programs, and collaborative tools that enable IT to safely empower business users.
Challenges:
- Governance and IT Oversight: Managing applications built by citizen developers, ensuring they adhere to security policies, data standards, and architectural guidelines, and preventing the sprawl of unmanaged applications ("app chaos") is a significant governance challenge for IT departments.
- Security Vulnerabilities in Generated Code: While platforms aim for security, the underlying code generated by low-code tools might still contain vulnerabilities if not properly audited or if developers inadvertently introduce flaws through custom logic. Ensuring end-to-end security remains paramount.
- Technical Debt Management: Rapid development can sometimes lead to accumulating technical debt if applications are built quickly without sufficient architectural foresight or if quick fixes are prioritized over sustainable solutions. Managing this debt can become a challenge over time.
- Integration with Existing IT Ecosystems: Despite improvements, ensuring seamless, robust, and scalable integration of low-code applications with an organization's diverse and often complex existing IT infrastructure (CRMs, ERPs, databases, APIs) continues to be a major technical challenge.
- Talent Development for Hybrid Teams: As low-code blurs the lines between professional developers and citizen developers, the challenge lies in fostering a hybrid development culture, defining clear roles, and providing adequate training for both groups to collaborate effectively.
- Performance Optimization and Debugging Complex Applications: Debugging and optimizing the performance of complex applications built on low-code platforms can be challenging, as the underlying code may be abstracted from the developer, making it harder to pinpoint and resolve performance bottlenecks.
- Overcoming Resistance from Traditional Developers: Some professional developers may resist low-code platforms, viewing them as a threat to their skillset or as tools that limit their creativity and control. Overcoming this resistance and demonstrating the value of low-code as an augmentation tool, rather than a replacement, is crucial for widespread adoption
Low-Code Development Platform Market: Report Scope
This report thoroughly analyzes the Low-Code Development Platform Market, exploring its historical trends, current state, and future projections. The market estimates presented result from a robust research methodology, incorporating primary research, secondary sources, and expert opinions. These estimates are influenced by the prevailing market dynamics as well as key economic, social, and political factors. Furthermore, the report considers the impact of regulations, government expenditures, and advancements in research and development on the market. Both positive and negative shifts are evaluated to ensure a comprehensive and accurate market outlook.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Low-Code Development Platform Market |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 22.18 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2032 | USD 213.22 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 28.59% |
| Number of Pages | 110 |
| Key Companies Covered | AgilePoint Inc., Caspio, Inc., Appian, Bizagi, Kony, Inc., LucidArt AB, Mendix Tech BV, Oracle Corporation, Microsoft, Netcall, Google, LLC, OutSystems, Salesforce.com, Inc., SourceCode Technology Holdings, Inc., Zoho Corporation, and Others |
| Segments Covered | By Deployment Model, By Component, By Organization Size, By Industry, And By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historical Year | 2018 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2024 to 2032 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Low-Code Development Platform Market: Segmentation Insights
The global low-code development platform market is divided by application type, deployment type, organization size, end-use, and region.
Segmentation Insights by Application Type
Based on application type, the global low-code development platform market is divided into web-based and mobile-based.
Web-based applications dominate the Low-Code Development Platform Market due to their universal accessibility, ease of deployment, and broad applicability across industries. These platforms allow developers and business users to build responsive, browser-based applications without deep coding knowledge, making them ideal for customer portals, internal dashboards, e-commerce platforms, and business process automation tools. The demand for digital transformation in areas like finance, healthcare, education, and retail continues to propel web-based solutions, as organizations prioritize agility and scalability. Moreover, web-based applications can be updated in real time and accessed from multiple devices, reducing IT maintenance burdens and improving user experience. The growing adoption of SaaS models and the shift toward cloud-first strategies further cement the leadership of web-based applications in the low-code ecosystem.
Mobile-based applications form a rapidly expanding segment, driven by the global increase in smartphone usage and the need for on-the-go enterprise solutions. Low-code platforms supporting mobile application development enable businesses to quickly launch apps for field services, remote workforce management, customer engagement, and real-time data access. These platforms typically offer features such as drag-and-drop interfaces, device compatibility, offline functionality, and integration with mobile-specific APIs. While mobile-based development has historically required more specialized skills, low-code tools are lowering that barrier, expanding the reach to non-technical users and accelerating time to market. Although mobile-based applications trail web-based apps in market share, their growth trajectory is strong due to the increasing emphasis on mobile-first digital strategies across sectors.
Segmentation Insights by Deployment Type
On the basis of deployment type, the global low-code development platform market is bifurcated into cloud and on-premise.
Cloud deployment dominates the Low-Code Development Platform Market due to its scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, making it the preferred choice for organizations of all sizes, especially those undergoing digital transformation. Cloud-based platforms enable users to access development environments from anywhere, collaborate in real-time, and deploy applications rapidly without the burden of managing infrastructure. This model supports faster updates, automatic scaling, and seamless integration with cloud-native services like databases, APIs, and identity providers. Cloud deployment is also favored for its lower upfront investment, predictable subscription pricing, and alignment with DevOps and agile practices. As businesses increasingly migrate to cloud ecosystems such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, demand for cloud-native low-code tools continues to rise, reinforcing its leading position in the market.
On-premise deployment serves a more specialized segment of the market, primarily organizations with strict data governance, security, and compliance requirements—such as those in government, defense, healthcare, and banking. These organizations prioritize full control over their development environments and data infrastructure, often to meet internal policies or regulatory mandates. On-premise platforms offer deeper customization capabilities and tighter integration with legacy systems, which is critical for enterprises with established IT ecosystems. While on-premise adoption is slower compared to cloud, it remains relevant among large enterprises and institutions that demand high-security, mission-critical deployments with minimal reliance on external networks.
Segmentation Insights by Organization Size
On the basis of organization size, the global low-code development platform market is bifurcated into SME and large enterprise.
Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) dominate the Low-Code Development Platform Market due to their need for rapid digital transformation with limited technical and financial resources. SMEs often lack large in-house IT departments and require efficient ways to build, deploy, and maintain applications. Low-code platforms enable these businesses to create customized solutions—such as CRM systems, inventory management tools, and customer portals—without relying heavily on professional developers. The drag-and-drop interfaces, pre-built modules, and integration capabilities offered by low-code solutions allow SMEs to improve business agility, streamline operations, and enhance customer engagement. Furthermore, the affordability and subscription-based pricing of most low-code platforms make them especially attractive for cost-conscious SMEs looking to scale without major capital investments.
Large Enterprises form a significant but slightly trailing segment in the low-code market, driven by their need to modernize legacy systems, enhance operational efficiency, and meet increasing demands for digital services. These organizations use low-code platforms to augment traditional development processes, accelerate time-to-market, and empower business units to build apps independently through citizen development. Large enterprises typically leverage low-code tools for internal applications, process automation, and departmental solutions, while integrating them with complex IT ecosystems. Although they have the resources for custom software development, the push for innovation, agility, and reduced development backlogs has made low-code an essential part of their broader digital strategy.
Segmentation Insights by End-use
On the basis of end-use, the global low-code development platform market is bifurcated into BFSI, retail, education, it & telecom, transportation & logistics, and others.
BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) dominates the Low-Code Development Platform Market owing to the industry's pressing need for fast, secure, and compliant digital solutions. Financial institutions increasingly rely on low-code platforms to accelerate the development of customer-facing applications, streamline internal workflows, and comply with rapidly evolving regulatory standards. Low-code tools allow banks and insurers to automate loan processing, claims management, customer onboarding, and fraud detection systems with reduced time-to-market. The sector also benefits from enhanced agility and integration with core banking systems, APIs, and data analytics engines. The rise of digital banking, fintech competition, and demand for mobile-first solutions further solidifies BFSI’s lead in adopting low-code platforms.
Automotive & Manufacturing leverages low-code platforms to digitize operational processes, from production planning and quality assurance to supply chain coordination and inventory tracking. These industries utilize low-code solutions to build custom applications that improve factory automation, monitor performance metrics, and enable real-time reporting, especially as Industry 4.0 technologies become more prevalent. The ability to rapidly iterate on applications without deep coding skills allows manufacturing firms to remain responsive to changes in demand, safety compliance, and logistics disruptions.
Retail uses low-code platforms to drive omnichannel engagement, streamline backend operations, and personalize customer experiences. Retailers deploy low-code tools for order management systems, loyalty programs, mobile POS solutions, and customer support automation. As e-commerce expands and consumers demand faster, more tailored interactions, low-code platforms help retail businesses rapidly deploy changes and integrate customer data across platforms.
Education institutions adopt low-code tools to create and manage student portals, digital learning management systems, and administrative automation such as admissions, grading, and scheduling. With growing demand for hybrid learning models, institutions rely on low-code platforms to quickly respond to evolving educational delivery needs, improve resource planning, and facilitate better student-teacher engagement through digital interfaces.
IT & Telecom companies implement low-code platforms to enhance internal application development, manage IT service requests, automate workflows, and improve customer self-service capabilities. Telecom providers, in particular, use low-code to speed up the deployment of new digital services, optimize field operations, and enhance network monitoring tools. These platforms offer modularity and speed without compromising the complex architecture needs of IT-heavy environments.
Transportation & Logistics benefits from low-code development by building real-time tracking systems, fleet management dashboards, and warehouse optimization tools. These platforms allow logistics companies to digitize delivery workflows, manage route planning, and respond dynamically to disruptions. Given the sector’s growing need for agility and operational efficiency, low-code tools support rapid customization and integration with IoT and GPS-based tracking systems.
Low-Code Development Platform Market: Regional Insights
- North America is expected to dominate the global market
North America is the dominant region in the global low-code development platform market, driven by early enterprise adoption, a highly skilled IT workforce, and the presence of major technology vendors such as Microsoft, Salesforce, Appian, Mendix, and OutSystems. Enterprises across industries—including banking, healthcare, manufacturing, and public sector—adopt low-code tools to accelerate digital transformation, automate workflows, and reduce software development time and cost. The region's strong focus on cloud-native architecture, API-first development, and DevOps integration has enabled widespread deployment of low-code platforms for both citizen developers and professional IT teams. Moreover, compliance with regulatory frameworks (such as HIPAA, SOX, and GDPR for U.S.-based international operations) has spurred demand for secure and scalable low-code solutions. Organizations increasingly use these platforms to build internal apps, automate legacy processes, and develop customer-facing portals with minimal coding, reinforcing North America’s leadership in terms of technological maturity and market penetration.
Europe represents a significant and steadily growing market for low-code development platforms. Countries such as Germany, the UK, France, and the Netherlands are key adopters, where low-code tools are used for enhancing business agility and enabling cross-functional teams to develop applications. Adoption is driven by a shortage of skilled developers, increasing need for rapid application delivery, and the rise of remote and hybrid work models. European enterprises focus heavily on compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, making security and data sovereignty critical features in platform selection. Many companies in Europe use low-code solutions for process digitization, integration with legacy ERP systems, and front-end interface development. However, concerns over vendor lock-in, limited customization, and cloud data residency regulations still moderate the pace of growth compared to North America.
Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a rapidly expanding market for low-code development, with major growth centers in China, India, Japan, South Korea, and Australia. Enterprises in sectors such as telecom, banking, and logistics use low-code platforms to digitize customer interactions, automate back-office processes, and reduce dependence on conventional software development cycles. In India, the strong presence of IT services firms and start-ups fuels local innovation and adoption of low-code frameworks. China, meanwhile, focuses on domestic platforms tailored to regulatory and linguistic requirements. However, challenges such as inconsistent infrastructure, fragmented IT ecosystems, and limited standardization can hinder full-scale deployment. Compared to North America, Asia-Pacific remains behind in enterprise-wide platform integration and governance maturity but is catching up rapidly due to strong cloud adoption and mobile-first development priorities.
Latin America is witnessing gradual growth in low-code adoption, primarily in Brazil, Mexico, Chile, and Colombia. Regional businesses are turning to low-code solutions to bridge IT skill gaps, automate manual processes, and support digital service delivery. SMEs in particular favor low-code platforms for developing customer portals, internal dashboards, and business automation tools. While cloud readiness and digital transformation efforts are progressing, budget constraints, legacy dependencies, and lack of regional vendor presence limit broader market maturity. North America remains far ahead in terms of ecosystem development, vendor diversity, and platform innovation.
Middle East & Africa are still in the early stages of adopting low-code development platforms, with the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and South Africa as key developing markets. In the Middle East, government digitalization initiatives and smart city projects are encouraging adoption of application platforms that support rapid deployment and cross-platform integration. African countries, meanwhile, face infrastructure and skills challenges that slow adoption. Despite growing interest among enterprises seeking faster digital rollouts, the region lacks the comprehensive vendor support and market penetration found in North America.
Low-Code Development Platform Market: Competitive Landscape
The report provides an in-depth analysis of companies operating in the low-code development platform market, including their geographic presence, business strategies, product offerings, market share, and recent developments. This analysis helps to understand market competition.
Some of the major players in the global low-code development platform market include:
- AgilePoint Inc.
- Caspio Inc.
- Appian
- Bizagi
- Kony Inc.
- LucidArt AB
- Mendix Tech BV
- Oracle Corporation
- Microsoft
- Netcall
- Google LLC
- OutSystems
- Salesforce.com Inc.
- SourceCode Technology Holdings Inc.
- Zoho Corporation
- Creatio
- LANSA
- Pegasystems Inc.
- Quickbase
- ServiceNow
The global low-code development platform market is segmented as follows:
By Application Type
- Web-based
- Mobile-based
By Deployment Type
- Cloud
- On-premise
By Organization Size
- SME
- Large Enterprise
By End-use
- BFSI
- Automotive & Manufacturing
- Retail
- Education
- IT & Telecom
- Transportation & Logistics
- Others
By Region
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Rest of Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Table Of Content
Inquiry For Buying
Low-Code Development Platform
Request Sample
Low-Code Development Platform