LTE Femto Base Station Market Size, Share, and Trends Analysis Report
CAGR :

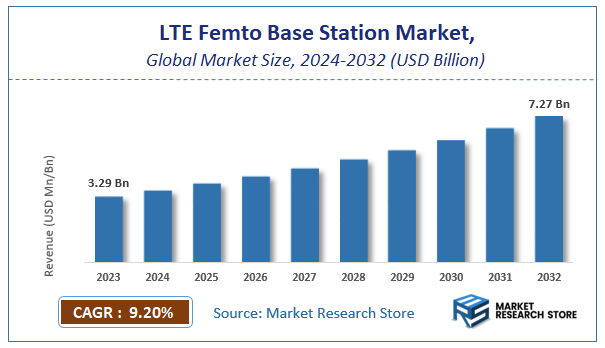
| Market Size 2023 (Base Year) | USD 3.29 Billion |
| Market Size 2032 (Forecast Year) | USD 7.27 Billion |
| CAGR | 9.2% |
| Forecast Period | 2024 - 2032 |
| Historical Period | 2018 - 2023 |
LTE Femto Base Station Market Insights
According to Market Research Store, the global LTE femto base station market size was valued at around USD 3.29 billion in 2023 and is estimated to reach USD 7.27 billion by 2032, to register a CAGR of approximately 9.2% in terms of revenue during the forecast period 2024-2032.
The LTE femto base station report provides a comprehensive analysis of the market, including its size, share, growth trends, revenue details, and other crucial information regarding the target market. It also covers the drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges till 2032.
To Get more Insights, Request a Free Sample
Global LTE Femto Base Station Market: Overview
An LTE femto base station, also known as a femtocell, is a small, low-power cellular base station that operates within a home or small office environment, offering enhanced coverage and capacity for LTE (Long-Term Evolution) networks. It connects to the service provider's network via broadband (e.g., DSL, cable, or fiber optic) and provides localized cellular coverage, typically for a few users. LTE femto base stations are designed to improve indoor network coverage, especially in areas where traditional macro-cell coverage is weak or unavailable, such as in basements or densely populated buildings.
Key Highlights
- The LTE femto base station market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 9.2% during the forecast period.
- The global LTE femto base station market was estimated to be worth approximately USD 3.29 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a value of USD 7.27 billion by 2032.
- The growth of the LTE femto base station market is being driven by increasing demand for better indoor coverage, reduced network congestion, and enhanced user experiences in areas with high mobile data consumption.
- Based on the component, the hardware segment is growing at a high rate and is projected to dominate the market.
- On the basis of technology, the frequency division duplex (FDD) segment is projected to swipe the largest market share.
- In terms of network type, the femto network segment is expected to dominate the market.
- Based on the deployment type, the indoor deployment segment is expected to dominate the market.
- In terms of end-use industry, the residential segment is expected to dominate the market.
- By region, Asia Pacific is expected to dominate the global market during the forecast period.
LTE Femto Base Station Market: Dynamics
Key Growth Drivers:
- Growing Demand for Enhanced Indoor Coverage and Capacity: LTE femto base stations are small, low-power cellular base stations designed to improve mobile signal coverage and capacity within limited areas like homes, offices, and small businesses. The increasing demand for seamless indoor connectivity and higher data rates drives their adoption.
- Offloading Macro Network Traffic: Femtocells can offload data traffic from the macro cellular network, especially in densely populated areas or buildings with poor signal penetration. This helps mobile operators improve network performance and user experience without significant macro network upgrades.
- Cost-Effective Solution for Coverage Extension: Deploying femtocells can be a more cost-effective way for mobile operators to extend their coverage into underserved indoor locations compared to deploying traditional macro base stations or distributed antenna systems (DAS).
- Support for High-Bandwidth Applications: The increasing use of bandwidth-intensive applications like video streaming, online gaming, and video conferencing necessitates better indoor capacity, which LTE femtocells can provide.
- Simplified Deployment and Self-Configuration: Modern LTE femtocells often feature simplified deployment processes, including plug-and-play functionality and self-configuration capabilities, making them easier for end-users or small businesses to install.
Restraints:
- Interference Management with Macro Networks: Ensuring that femtocells do not cause significant interference with the macro cellular network and vice versa requires sophisticated interference management techniques and careful network planning.
- Security Concerns: Deploying numerous small base stations raises security concerns regarding unauthorized access and potential vulnerabilities, requiring robust security protocols and management systems.
- Backhaul Connectivity Requirements: Femtocells require reliable backhaul connectivity (typically broadband internet access) to connect to the mobile operator's core network. The availability and quality of broadband can be a limiting factor in some areas.
- Regulatory Hurdles and Spectrum Allocation: Obtaining necessary regulatory approvals and managing spectrum allocation for a large number of femtocells can be complex and time-consuming for mobile operators.
- Power Consumption: While low-power compared to macro cells, the cumulative power consumption of a large number of deployed femtocells can still be a concern for both end-users and operators.
Opportunities:
- Integration with Enterprise Networks: LTE femtocells can be integrated with enterprise WLAN and LAN networks to provide seamless mobility and unified communication services within organizations.
- Neutral Host Deployments: The concept of neutral host femtocells, which can support multiple mobile operators, offers opportunities for wider adoption and reduced deployment costs for individual carriers.
- Value-Added Services: Femtocells can serve as a platform for delivering location-based services, targeted advertising, and other value-added applications within their coverage area.
- Private LTE Networks: The growing interest in private LTE networks for industrial and enterprise applications presents an opportunity for deploying femtocells to provide dedicated and secure wireless connectivity.
- Advancements in Self-Organizing Network (SON) Technologies: SON technologies can automate the configuration, optimization, and troubleshooting of large-scale femtocell deployments, simplifying management and reducing operational costs.
Challenges:
- Scalability and Management of Large Deployments: Managing and maintaining a large number of distributed femtocells can be complex, requiring robust network management systems and efficient troubleshooting tools.
- Cost Competitiveness Against Other Indoor Coverage Solutions: Femtocells compete with other indoor coverage solutions like Wi-Fi extension, DAS, and small cells. Their cost-effectiveness and performance need to be competitive.
- End-User Adoption and Awareness: Educating consumers and businesses about the benefits and ease of use of LTE femtocells is crucial for driving adoption.
- Ensuring Quality of Service (QoS): Providing consistent and reliable QoS for users connected through femtocells, especially during peak usage times, can be challenging and requires effective resource management.
- Interoperability and Standardization: Ensuring interoperability between femtocells from different vendors and with various macro network equipment is essential for seamless network operation.
- Addressing Potential Health Concerns: While generally operating at low power levels, addressing any potential public health concerns related to radio frequency emissions from a large number of femtocells is important for public acceptance.
LTE Femto Base Station Market: Report Scope
This report thoroughly analyzes the LTE Femto Base Station Market, exploring its historical trends, current state, and future projections. The market estimates presented result from a robust research methodology, incorporating primary research, secondary sources, and expert opinions. These estimates are influenced by the prevailing market dynamics as well as key economic, social, and political factors. Furthermore, the report considers the impact of regulations, government expenditures, and advancements in research and development on the market. Both positive and negative shifts are evaluated to ensure a comprehensive and accurate market outlook.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | LTE Femto Base Station Market |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 3.29 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2032 | USD 7.27 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 9.2% |
| Number of Pages | 176 |
| Key Companies Covered | Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, Samsung, NEC, Fujitsu, Airspan, Cisco Systems, CommScope, Motorola Solutions |
| Segments Covered | By Component, By Technology, By Network Type, By Deployment Type, By End-Use Industry, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historical Year | 2018 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2024 to 2032 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
LTE Femto Base Station Market: Segmentation Insights
The global LTE femto base station market is divided by component, technology, network type, deployment type, end-use industry, and region.
Segmentation Insights by Component
Based on component, the global LTE femto base station market is divided into hardware, software, and services.
In the LTE femto base station market, hardware emerges as the most dominant segment among the components. Hardware components such as antennas, signal processors, power amplifiers, and radio frequency (RF) modules form the physical foundation of femto base stations. The demand for compact, high-performance, and energy-efficient hardware solutions has grown significantly due to the increasing need for enhanced indoor mobile coverage and the rollout of 4G and 5G networks. Hardware holds dominance because it is essential for the physical deployment of femto base stations across homes, enterprises, and public spaces. The continuous innovation in semiconductor technology and the integration of multi-band support within small form-factor equipment further strengthen the hardware segment's position in the market.
The software segment follows hardware and plays a critical role in managing and optimizing femto base station operations. Software solutions enable tasks such as signal routing, interference management, load balancing, and network security. As operators shift toward virtualization and cloud-based architectures, the importance of scalable and remotely upgradable software has risen. Although it does not surpass hardware in terms of market share, software is vital for the intelligent operation and customization of LTE femto base stations, especially in diverse user environments.
Services represent the smallest segment in the LTE femto base station market. This includes installation, maintenance, consulting, and managed services offered by telecom equipment providers and network operators. While necessary for ensuring operational continuity and customer satisfaction, services typically represent a smaller portion of overall revenue. However, the service segment is gradually growing as telecom operators increasingly outsource network optimization and technical support to third-party providers to reduce operational costs and improve service quality.
Segmentation Insights by Technology
On the basis of technology, the global LTE femto base station market is bifurcated into time division duplex (TDD), frequency division duplex (FDD), and long-term evolution (LTE).
In the LTE femto base station market, Frequency Division Duplex (FDD) stands as the most dominant technology segment. FDD enables simultaneous two-way communication by using separate frequency bands for uplink and downlink, ensuring minimal latency and better quality of service. Its widespread adoption in commercial LTE deployments globally, especially in regions with abundant paired spectrum, has cemented its leading position. FDD is particularly favored in urban and suburban areas for its capacity to manage high traffic volumes and deliver consistent indoor coverage, making it a preferred choice for telecom operators and enterprises deploying femto cells.
The Time Division Duplex (TDD) segment follows FDD in terms of market share. TDD uses the same frequency band for both uplink and downlink but separates the two by time slots. This makes it more spectrum-efficient and adaptable in scenarios where traffic is asymmetric—such as in residential and public hotspot environments. TDD-based femto base stations are gaining popularity in markets like China and India, where unpaired spectrum allocations are more prevalent. While it lags behind FDD in global deployment, TDD is rapidly growing due to its flexibility and cost-efficiency.
Long-Term Evolution (LTE) as a standalone category is the foundational technology for both FDD and TDD. While FDD and TDD refer to duplexing methods within LTE, some reports classify “LTE” separately to cover broader femto base station functionalities, including multi-mode support and backward compatibility with 3G or 2G. In such cases, the "LTE" category typically refers to general-purpose femto base stations that support various LTE implementations without specifying a duplexing method. This segment may be smaller compared to the specific FDD and TDD technologies, but it is significant in mixed-network environments where flexibility across technologies is required.
Segmentation Insights by Network Type
Based on network type, the global LTE femto base station market is divided into macro network, micro network, pico network, and femto network.
In the LTE femto base station market, the Femto Network segment is, unsurprisingly, the most dominant network type. Femto networks are specifically designed for small-scale, localized coverage such as in homes, small offices, and indoor public areas. These networks utilize femto base stations to improve indoor coverage and offload traffic from the macro network, particularly in high-density environments. Their ability to support high data rates and enhance user experience while being cost-effective makes femto networks the primary focus of this market. The surge in mobile data usage and the demand for improved indoor connectivity drive the dominance of this segment.
The Pico Network segment comes next in terms of market relevance. Pico networks use pico base stations, which cover a slightly larger area than femto cells, such as shopping malls, hospitals, or enterprise campuses. These networks are beneficial in semi-public or enterprise settings where a higher number of simultaneous connections is required. Although not as widely deployed in residential settings as femto networks, pico networks play a significant role in providing consistent LTE coverage in commercial environments.
Micro Networks follow, typically deployed in outdoor environments or large venues like stadiums, city centers, or transit hubs. These networks use micro base stations with broader coverage than pico and femto cells but are still considered part of the small cell family. In the context of the LTE femto base station market, micro networks are less directly relevant but may complement femto deployments in larger, integrated small cell strategies.
Lastly, Macro Networks represent the traditional large-scale cellular infrastructure with wide area coverage. While critical for overall LTE deployment, macro networks are the least relevant in this specific market segment focused on femto base stations. They are often used in conjunction with femto networks to ensure seamless connectivity, but their role in the femto base station market is indirect, mainly as part of the overarching network architecture.
Segmentation Insights by Deployment Type
On the basis of deployment type, the global LTE femto base station market is bifurcated into indoor deployment and outdoor deployment.
In the LTE femto base station market, indoor deployment is the most dominant deployment type. Femtocells are specifically designed to enhance indoor cellular coverage where macro networks often struggle due to building materials and structural interference. Homes, offices, shopping centers, hospitals, and educational institutions are common locations for indoor femto base stations. These environments demand consistent, high-speed mobile connectivity, especially with the growing reliance on smartphones and IoT devices. The dominance of indoor deployment is driven by the need to offload network traffic from congested macro cells and provide reliable service quality inside buildings.
Outdoor deployment, while less prevalent, is a growing segment—particularly in scenarios where macro network coverage is weak or where densification is needed without installing large infrastructure. Outdoor femto base stations are typically used in small public areas, rural zones, or dense urban pockets where gaps in coverage persist. They are built to withstand environmental conditions and provide targeted network enhancements. Although outdoor deployment contributes a smaller share to the overall market, its importance is rising with the expansion of smart cities and the need for seamless connectivity across all environments.
Segmentation Insights by End-Use Industry
On the basis of end-use industry, the global LTE femto base station market is bifurcated into residential, commercial, public sector, and transportation & logistics.
In the LTE femto base station market, the residential segment is the most dominant end-use industry. Residential users primarily deploy femto base stations to improve indoor mobile signal strength and data speeds, especially in areas where macro network coverage is weak or inconsistent. These compact base stations are ideal for homes due to their ease of installation, affordability, and the growing demand for high-bandwidth services such as video streaming, online gaming, and remote work. The surge in connected devices in households and the need for uninterrupted connectivity have cemented the residential sector's leading position in the market.
Following residential, the commercial segment holds a significant share of the market. Businesses—particularly small and medium enterprises—rely on femto base stations to enhance network performance within office buildings, retail stores, banks, and hotels. These environments often experience high user density and demand robust mobile connectivity to support voice, data, and business-critical applications. As enterprises increasingly adopt cloud services and remote collaboration tools, the need for secure and reliable in-building LTE coverage continues to grow.
The public sector segment includes government facilities, educational institutions, and healthcare centers that require secure and dedicated network infrastructure. Femtocells in these environments ensure operational continuity, improve service delivery, and support mission-critical communications. While not as large as residential or commercial, this segment is gaining traction due to smart government initiatives and the digitalization of public services.
The transportation & logistics segment represents the smallest share among the end-use industries. However, it is a niche but growing area where femto base stations are deployed in transportation hubs like airports, seaports, and railway stations to provide localized coverage and support real-time logistics tracking and communication. As smart transportation systems evolve and require seamless connectivity, the adoption of femto base stations in this sector is expected to rise, although it currently lags behind other segments in terms of market penetration.
LTE Femto Base Station Market: Regional Insights
- Asia Pacific is expected to dominates the global market
The Asia Pacific region is the most dominant in the LTE femto base station market, driven by its large population base, rapid digitalization, and aggressive investment in telecommunications infrastructure. Countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea lead the charge with advanced deployments of LTE and ongoing transition to 5G networks. China, in particular, plays a critical role due to its government-backed initiatives aimed at expanding mobile connectivity and smart city projects. The increasing demand for enhanced indoor coverage and low-latency communication in urban areas contributes significantly to the growth of femto base station deployment across this region.
The North America market holds a strong position, fueled by early technological adoption, widespread LTE coverage, and a mature telecom ecosystem. The United States is the key contributor, where major telecom companies are actively deploying LTE femto base stations to address indoor coverage issues and support the growing number of connected devices. The region also benefits from high consumer demand for high-speed mobile data and the early adoption of IoT applications, all of which require improved network performance and reliability.
The Europe region demonstrates steady growth in the LTE femto base station market due to the focus on enhancing mobile connectivity across both urban and rural areas. Regulatory support for improving broadband access and bridging the digital divide is pushing telecom operators to adopt small cell technologies like femto base stations. Furthermore, initiatives to promote energy efficiency and smart grid integration in wireless communication infrastructure contribute to the market’s expansion in this region.
The Latin America region is gradually advancing in the LTE femto base station market as mobile internet usage increases and urbanization accelerates. Countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina are prioritizing telecom infrastructure improvements to meet rising demand for better connectivity. However, market growth is somewhat constrained by economic volatility and uneven network development, though efforts to expand 4G LTE coverage are creating future opportunities for femto base station deployment.
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) region remains the least dominant but is showing signs of potential as digital transformation gains momentum. Countries such as the UAE and Saudi Arabia are actively pursuing smart city projects and expanding LTE infrastructure, which supports the growth of femto base stations. In Africa, despite infrastructure challenges, increasing mobile penetration and efforts to improve rural connectivity are expected to slowly stimulate market development in the coming years.
LTE Femto Base Station Market: Competitive Landscape
The report provides an in-depth analysis of companies operating in the LTE femto base station market, including their geographic presence, business strategies, product offerings, market share, and recent developments. This analysis helps to understand market competition.
Some of the major players in the global LTE femto base station market include:
- Huawei
- Ericsson
- Nokia
- ZTE
- Samsung
- NEC
- Fujitsu
- Airspan
- Cisco Systems
- CommScope
- Motorola Solutions
The global LTE femto base station market is segmented as follows:
By Component
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Technology
- Time Division Duplex (TDD)
- Frequency Division Duplex (FDD)
- Long-Term Evolution (LTE)
By Network Type
- Macro Network
- Micro Network
- Pico Network
- Femto Network
By Deployment Type
- Indoor Deployment
- Outdoor Deployment
By End-Use Industry
- Residential
- Commercial
- Public Sector
- Transportation and Logistics
By Region
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Rest of Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Table Of Content
Inquiry For Buying
LTE Femto Base Station
Request Sample
LTE Femto Base Station
