Power Module for Electric Vehicle Market Size, Share, and Trends Analysis Report
CAGR :

| Market Size 2023 (Base Year) | USD 1379.37 Million |
| Market Size 2032 (Forecast Year) | USD 3199.64 Million |
| CAGR | 9.8% |
| Forecast Period | 2024 - 2032 |
| Historical Period | 2018 - 2023 |
Power Module for Electric Vehicle Market Insights
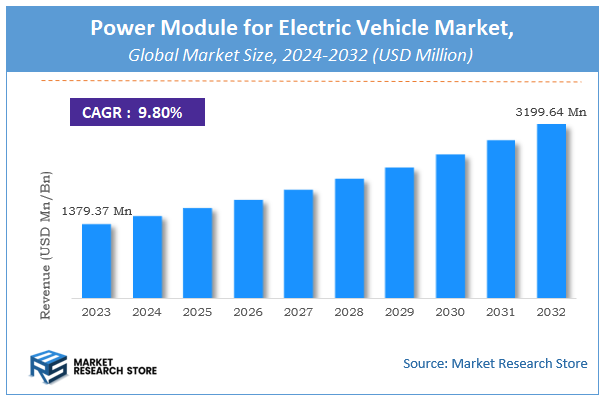
According to Market Research Store, the global power module for electric vehicle market size was valued at around USD 1379.37 million in 2023 and is estimated to reach USD 3199.64 million by 2032, to register a CAGR of approximately 9.8% in terms of revenue during the forecast period 2024-2032.
The power module for electric vehicle report provides a comprehensive analysis of the market, including its size, share, growth trends, revenue details, and other crucial information regarding the target market. It also covers the drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges till 2032.
To Get more Insights, Request a Free Sample
Global Power Module for Electric Vehicle Market: Overview
A power module for electric vehicles (EVs) is an integrated electronic component that plays a critical role in managing and converting electrical power within the vehicle’s propulsion system. It typically houses power semiconductor devices such as insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) or silicon carbide (SiC) transistors, along with drivers, control units, and sometimes cooling systems. These modules efficiently convert direct current (DC) from the battery to alternating current (AC) required by the motor, and vice versa during regenerative braking.
By doing so, they control the speed and torque of the electric motor, directly impacting the vehicle’s performance and energy efficiency. Power modules are designed to handle high voltages and currents while minimizing energy loss, thermal stress, and physical size, making them essential for enhancing the performance, range, and reliability of electric vehicles.
Key Highlights
- The power module for electric vehicle market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 9.8% during the forecast period.
- The global power module for electric vehicle market was estimated to be worth approximately USD 1379.37 million in 2023 and is projected to reach a value of USD 3199.64 million by 2032.
- The growth of the power module for electric vehicle market is being driven by the global shift toward sustainable transportation and the increasing adoption of EVs across both passenger and commercial segments.
- Based on the type of electric vehicle, the battery electric vehicles (BEVs) segment is growing at a high rate and is projected to dominate the market.
- On the basis of battery capacity, the above 60 kWh segment is projected to swipe the largest market share.
- In terms of vehicle class, the passenger cars segment is expected to dominate the market.
- Based on the charging infrastructure, the home charging stations segment is expected to dominate the market.
- In terms of end-user, the individual consumers segment is expected to dominate the market.
- By region, Asia Pacific is expected to dominate the global market during the forecast period.
Power Module for Electric Vehicle Market: Dynamics
Key Growth Drivers:
- Rising Adoption of Electric Vehicles (EVs): The global shift toward sustainable transportation is significantly boosting the demand for efficient power modules to improve vehicle performance and energy management.
- Advancements in Power Electronics Technology: Innovations in semiconductor materials like SiC (Silicon Carbide) and GaN (Gallium Nitride) are enhancing the efficiency, power density, and thermal performance of power modules.
- Government Incentives and Regulations Supporting EVs: Tax credits, subsidies, and strict emission regulations are encouraging both manufacturers and consumers to adopt EVs, thereby driving the need for reliable power modules.
- Increasing Demand for Fast Charging Solutions: Power modules that support higher voltage and efficient thermal management are crucial for enabling fast-charging infrastructure, which is increasingly in demand.
- Focus on Reducing Vehicle Weight and Improving Efficiency: Power modules help integrate multiple functions into compact units, reducing the size and weight of electronic systems and improving overall vehicle efficiency.
Restraints:
- High Cost of Advanced Power Modules: Materials like SiC and GaN are more expensive than traditional silicon, increasing the overall cost of power modules and posing affordability challenges for some manufacturers.
- Complex Design and Integration Requirements: Designing power modules for EVs requires addressing complex thermal, electrical, and mechanical challenges, which can slow down development and increase production time.
- Limited Infrastructure in Emerging Economies: Slower adoption of EVs in developing regions due to insufficient charging infrastructure indirectly limits the demand for power modules.
Opportunities:
- Emergence of 800V EV Architectures: The industry shift toward high-voltage EV platforms opens opportunities for next-generation power modules with better thermal performance and power density.
- Expansion into Commercial EVs: Growth in electric buses, trucks, and delivery vans presents a large untapped market for durable and high-performance power modules.
- Collaborations and Strategic Partnerships: Partnerships between automakers, semiconductor companies, and system integrators are fostering innovation and expanding market reach.
- Integration with Renewable Energy Systems: Power modules designed for bi-directional charging and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies offer new applications beyond mobility, such as energy storage and grid support.
Challenges:
- Thermal Management Issues: As power density increases, effectively dissipating heat becomes more difficult, which can compromise module reliability and performance.
- Standardization and Compatibility Issues: Lack of standardization across EV platforms can complicate module design and limit interoperability between components from different vendors.
- Supply Chain Constraints: Shortages in raw materials and semiconductor components can delay production timelines and affect the availability of power modules.
- Rapid Technological Obsolescence: The fast pace of innovation in EV power electronics can make existing designs outdated quickly, putting pressure on manufacturers to continuously invest in R&D.
Power Module for Electric Vehicle Market: Report Scope
This report thoroughly analyzes the Power Module for Electric Vehicle Market, exploring its historical trends, current state, and future projections. The market estimates presented result from a robust research methodology, incorporating primary research, secondary sources, and expert opinions. These estimates are influenced by the prevailing market dynamics as well as key economic, social, and political factors. Furthermore, the report considers the impact of regulations, government expenditures, and advancements in research and development on the market. Both positive and negative shifts are evaluated to ensure a comprehensive and accurate market outlook.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Power Module for Electric Vehicle Market |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 1379.37 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2032 | USD 3199.64 Million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 9.8% |
| Number of Pages | 184 |
| Key Companies Covered | Mitsubishi Electric, Fuji Electric, SEMIKRON, ON Semiconductor, Renesas Electronics, Vishay Intertechnology, Texas Instruments, Toshiba, Stmicroelectronics, NXP Semiconductors, Microsemi Corporation |
| Segments Covered | By Type of Electric Vehicle, By Battery Capacity, By Vehicle Class, By Charging Infrastructure, By End-User, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historical Year | 2018 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2024 to 2032 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Power Module for Electric Vehicle Market: Segmentation Insights
The global power module for electric vehicle market is divided by type of electric vehicle, battery capacity, vehicle class, charging infrastructure, end-user, and region.
Segmentation Insights by Type of Electric Vehicle
Based on type of electric vehicle, the global power module for electric vehicle market is divided into battery electric vehicles (BEVs), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), and advanced electric vehicles (AEVs).
In the power module for electric vehicle market, the Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) segment holds the dominant position. This dominance is largely due to the growing consumer and government push for zero-emission vehicles, along with advancements in battery technology and decreasing battery costs. BEVs rely entirely on electricity for propulsion and require efficient power modules to manage energy transfer between the battery and the drivetrain. As infrastructure for EV charging expands globally, the BEV segment continues to see the highest adoption, particularly in markets like China, Europe, and the United States.
Next in prominence are the Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs). These vehicles combine an internal combustion engine with an electric propulsion system but cannot be charged externally. HEVs rely heavily on power modules to optimize power usage between the engine and electric motor. Their popularity is driven by fuel efficiency and lower emissions compared to traditional ICE vehicles, especially in regions where charging infrastructure for BEVs is still developing.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) follow closely behind HEVs. These vehicles offer the flexibility of being charged via external power sources while still retaining an internal combustion engine. Power modules in PHEVs play a crucial role in managing complex power flows between the battery, engine, and electric motor. PHEVs appeal to consumers looking for electric range with the reassurance of fuel-based range extension, making them a transitional technology in the EV landscape.
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) represent a niche but technologically advanced segment. These vehicles generate electricity onboard using hydrogen fuel cells and emit only water as a byproduct. While power modules in FCEVs are vital for managing the power generated by the fuel cell stack, their adoption is limited due to high production costs and lack of hydrogen refueling infrastructure. Nevertheless, FCEVs are gaining traction in specific applications like heavy-duty transport and fleets.
At the emerging end of the spectrum are Advanced Electric Vehicles (AEVs), which include next-generation designs such as solar-powered EVs, extended-range electric vehicles (EREVs), and vehicles with integrated AI and autonomous driving capabilities. While currently the smallest segment, AEVs represent the future of EV innovation. Their power modules are often highly specialized to accommodate advanced features and multi-source energy systems, but the market presence remains limited due to technological maturity and high costs.
Segmentation Insights by Battery Capacity
On the basis of battery capacity, the global power module for electric vehicle market is bifurcated into below 20 kwh, 21 kwh to 40 kwh, 41 kwh to 60 kwh, and above 60 kwh.
In the power module for electric vehicle market, segmentation by battery capacity reveals that the Above 60 kWh category is the most dominant segment. This dominance is driven by the growing demand for long-range electric vehicles, particularly in the passenger and premium vehicle segments. Larger battery capacities support extended driving ranges, which address range anxiety—a key concern among EV consumers. Vehicles in this category, such as high-end BEVs and electric SUVs, require more sophisticated and high-capacity power modules to manage thermal efficiency, power distribution, and fast charging requirements, making them a major driver of growth in this market.
The 41 kWh to 60 kWh segment is the next most significant. It includes many mid-range electric vehicles that strike a balance between affordability and performance. Power modules in this capacity range are critical in ensuring efficient battery management and energy delivery, especially for city commuters and fleet applications. This segment is popular in both developed and emerging markets, offering practical range and cost-effectiveness.
Following this is the 21 kWh to 40 kWh segment, which caters primarily to compact EVs and urban-focused electric cars. These vehicles prioritize low weight and efficiency over range, making them suitable for short-distance travel. Power modules for this capacity are typically simpler and less expensive, which supports adoption in budget-conscious markets and for purposes such as shared mobility or local deliveries.
The Below 20 kWh category represents the smallest and least dominant segment. This range is generally found in low-speed electric vehicles (LSEVs), electric two-wheelers, and microcars. Although power modules in this segment are less complex, the limited energy storage capacity restricts their application to niche markets or specific regional use cases with minimal range requirements. Growth in this segment is modest due to increasing consumer expectations for higher-range vehicles.
Segmentation Insights by Vehicle Class
Based on vehicle class, the global power module for electric vehicle market is divided into passenger cars, light commercial vehicles (LCVs), heavy commercial vehicles (HCVs), two-wheelers, and three-wheelers.
In the power module for electric vehicle market, segmentation by vehicle class shows that Passenger Cars are the most dominant segment. This dominance is fueled by the massive global shift toward electrification of personal mobility, supported by favorable government policies, subsidies, and expanding charging infrastructure. Power modules used in passenger EVs must be compact, efficient, and capable of managing medium to high power loads for acceleration, heating/cooling, and auxiliary systems. The high production volume of electric passenger cars makes this segment the key driver for the power module market.
Following passenger cars are Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs), including electric vans and delivery trucks. The surge in e-commerce and the push for sustainable logistics solutions have significantly increased the demand for electric LCVs. Power modules in this class are engineered for higher payload efficiency and longer duty cycles, and must deliver reliability under commercial operating conditions. This segment is gaining momentum especially in urban and last-mile delivery applications.
Heavy Commercial Vehicles (HCVs) represent the next segment. Although their current market share is smaller, it is growing steadily due to increasing adoption of electric buses, trucks, and logistics fleets. Power modules for HCVs are robust and high-capacity, designed to handle significant energy demands and thermal loads. The complexity and cost of electrifying heavy vehicles are higher, but supportive policies and technological advancements are accelerating growth in this area.
Two-Wheelers form a sizeable but more regionally concentrated segment, especially prevalent in Asia-Pacific markets like India, China, and Southeast Asia. Electric scooters and motorcycles use smaller power modules with basic thermal and power management. Their affordability, ease of use, and lower energy requirements make them ideal for short-range personal and delivery applications.
Three-Wheelers, while the smallest segment globally, play an important role in urban transport and goods movement in developing regions. Electrification in this category is driven by low operating costs and government incentives for cleaner public transportation. Power modules in electric three-wheelers are relatively simple but must be rugged and cost-effective for frequent short trips.
Segmentation Insights by Charging Infrastructure
On the basis of charging infrastructure, the global power module for electric vehicle market is bifurcated into home charging stations, public charging stations, fast charging stations, wireless charging solutions, and battery swapping stations.
In the power module for electric vehicle market, segmentation by charging infrastructure reveals that Home Charging Stations dominate the market. Most electric vehicle owners prefer the convenience of charging their vehicles at home, particularly overnight. This segment’s growth is propelled by increasing EV adoption in residential areas, government incentives for home charger installations, and improvements in smart charging technology. Power modules used in this context are optimized for AC charging with moderate power levels and are designed for efficiency, safety, and affordability.
Public Charging Stations are the next most dominant segment, driven by the need for accessible charging in urban areas, workplaces, and commercial centers. Power modules here are more robust than those in home chargers, supporting both AC and DC charging with higher power requirements. The growth of this segment is tied closely to government and private investments in public infrastructure, aiming to reduce range anxiety and support widespread EV adoption.
Fast Charging Stations follow as a key growth segment. These stations are critical for enabling long-distance travel and minimizing charging downtime, especially for fleets and highway users. Power modules in fast charging stations are high-capacity and must handle significant thermal and power management challenges. While the installation cost is high, advancements in high-voltage architecture and battery technologies are making this option more viable.
Wireless Charging Solutions are an emerging and innovative segment with strong potential. Though currently limited in adoption due to high costs and technological complexity, wireless charging offers unmatched convenience. Power modules in these systems must efficiently manage inductive power transfer, safety mechanisms, and dynamic vehicle alignment. Growth is expected in premium EVs and autonomous vehicle segments as the technology matures.
Battery Swapping Stations represent a niche but growing segment, especially in regions like China and India where rapid turnaround for commercial and two/three-wheeled EVs is critical. Instead of waiting to charge, users swap out depleted batteries for fully charged ones. Power modules in this ecosystem are used in charging the batteries behind the scenes and must support high-volume, fast-cycle operations with automated controls.
Segmentation Insights by End-User
On the basis of end-user, the global power module for electric vehicle market is bifurcated into individual consumers, commercial fleets, government agencies, ride-sharing services, and public transportation systems.
In the power module for electric vehicle market, segmentation by end-user highlights that Individual Consumers are the most dominant segment. This is driven by the rapid adoption of electric vehicles for personal use, particularly in urban and suburban regions. Individual consumers typically invest in home charging solutions and prefer vehicles that offer convenience, lower operational costs, and sustainability. Power modules for this segment focus on balancing cost, size, efficiency, and user-friendly features to enhance vehicle performance and reliability.
Following closely are Commercial Fleets, including delivery vans, service vehicles, and logistics operators. With the rise in e-commerce and pressure to decarbonize operations, fleet electrification has gained substantial traction. These users require power modules capable of managing higher usage cycles, greater loads, and fast charging capabilities. Reliability, thermal management, and cost-efficiency are key priorities in this segment, especially for companies transitioning large fleets.
Public Transportation Systems are another significant and growing segment, especially as city governments move toward electrifying buses and municipal fleets to meet emissions targets. Power modules in this class must support high power loads and long operational hours while ensuring passenger safety and system redundancy. Government-backed funding and environmental regulations are accelerating adoption in this segment globally.
Ride-Sharing Services such as Uber, Lyft, and regional equivalents are increasingly electrifying their fleets to reduce operational costs and align with sustainability goals. These vehicles often require fast-charging compatibility and high uptime, pushing demand for durable and efficient power modules. While still growing, this segment is poised to expand rapidly in regions with strong ride-hailing markets and supportive EV infrastructure.
Lastly, Government Agencies represent a smaller but important segment. This includes the electrification of police vehicles, utility services, and administrative fleets. Although adoption is slower due to procurement cycles and budget constraints, government fleets often set the tone for broader public EV adoption. Power modules in this segment must meet stringent safety, durability, and operational standards.
Power Module for Electric Vehicle Market: Regional Insights
- Asia Pacific is expected to dominates the global market
Asia Pacific is the most dominant region in the power module for electric vehicle market. This dominance is driven by the presence of large-scale EV manufacturers, mature semiconductor industries, and strong governmental policies that favor electric mobility. Countries like China, Japan, and South Korea lead the way in production, innovation, and domestic EV adoption. The integration of power modules in high-volume EV production lines across this region reinforces its leadership position in the global market.
Europe ranks as the second most influential region, supported by aggressive environmental regulations, high EV penetration rates, and a robust network of charging infrastructure. Countries such as Germany, France, and the Netherlands have embraced electrification with clear government mandates and incentives. The presence of key automotive OEMs and semiconductor firms facilitates the development and deployment of advanced power module technologies tailored for European EV platforms.
North America holds a significant position in the market, particularly due to increasing EV sales in the United States and Canada. Federal support, investments in battery manufacturing, and growing interest in high-performance electric vehicles are key factors fueling demand for power modules. The region also benefits from the expansion of domestic EV brands and enhanced R&D efforts focused on improving power electronics.
Latin America shows steady growth potential in the power module for electric vehicle market, although its share remains smaller compared to the leading regions. Countries like Brazil and Mexico are gradually increasing their adoption of EVs, particularly in public transportation fleets. Government incentives and early-stage investments in electric mobility infrastructure contribute to the region’s emerging presence in the market.
Middle East and Africa is the least dominant region in this market due to limited EV adoption and underdeveloped infrastructure. However, there are signs of progress in countries like the UAE and South Africa, where pilot programs and green initiatives are starting to promote electric vehicle use. While growth is currently slow, the region has long-term opportunities as sustainability goals become more prominent.
Power Module for Electric Vehicle Market: Competitive Landscape
The report provides an in-depth analysis of companies operating in the power module for electric vehicle market, including their geographic presence, business strategies, product offerings, market share, and recent developments. This analysis helps to understand market competition.
Some of the major players in the global power module for electric vehicle market include:
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Fuji Electric
- SEMIKRON
- ON Semiconductor
- Renesas Electronics
- Vishay Intertechnology
- Texas Instruments
- Toshiba
- Stmicroelectronics
- NXP Semiconductors
- Microsemi Corporation
The global power module for electric vehicle market is segmented as follows:
By Type of Electric Vehicle
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
- Advanced Electric Vehicles (AEVs)
By Battery Capacity
- Below 20 kWh
- 21 kWh to 40 kWh
- 41 kWh to 60 kWh
- Above 60 kWh
By Vehicle Class
- Passenger Cars
- Light Commercial Vehicles (LCVs)
- Heavy Commercial Vehicles (HCVs)
- Two-Wheelers
- Three-Wheelers
By Charging Infrastructure
- Home Charging Stations
- Public Charging Stations
- Fast Charging Stations
- Wireless Charging Solutions
- Battery Swapping Stations
By End-User
- Individual Consumers
- Commercial Fleets
- Government Agencies
- Ride-Sharing Services
- Public Transportation Systems
By Region
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Rest of Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the projected market size of the Power Module for Electric Vehicle market from 2024 to 2032?
Table Of Content
Inquiry For Buying
Power Module for Electric Vehicle
Request Sample
Power Module for Electric Vehicle
