Solar Photovoltaic Market Size, Share, and Trends Analysis Report
CAGR :

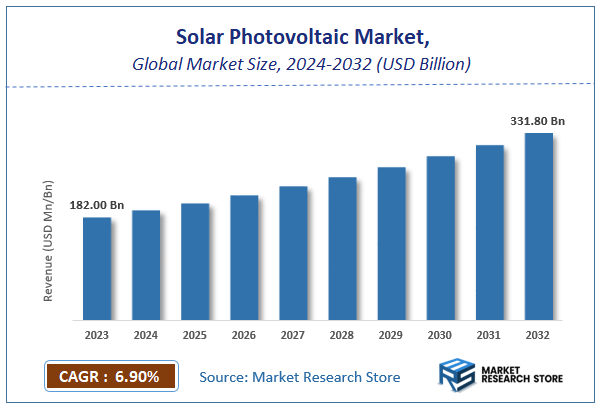
| Market Size 2023 (Base Year) | USD 182.00 Billion |
| Market Size 2032 (Forecast Year) | USD 331.80 Billion |
| CAGR | 6.9% |
| Forecast Period | 2024 - 2032 |
| Historical Period | 2018 - 2023 |
Solar Photovoltaic Market Insights
According to Market Research Store, the global solar photovoltaic market size was valued at around USD 182.00 billion in 2023 and is estimated to reach USD 331.80 billion by 2032, to register a CAGR of approximately 6.9% in terms of revenue during the forecast period 2024-2032.
The solar photovoltaic report provides a comprehensive analysis of the market, including its size, share, growth trends, revenue details, and other crucial information regarding the target market. It also covers the drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges till 2032.
Global Solar Photovoltaic Market: Overview
Solar photovoltaic (PV) technology is a method of converting sunlight directly into electricity using semiconductor materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect. These materials, typically silicon-based, absorb photons from sunlight and release electrons, generating an electric current. Solar PV systems consist of solar panels (modules), inverters, mounting structures, and balance-of-system components. They can be deployed in various configurations, including rooftop installations, ground-mounted solar farms, and portable solar devices, catering to residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications.
The growth of the solar photovoltaic market is driven by rising global demand for clean and renewable energy, decreasing costs of solar panels due to technological advancements and economies of scale, and supportive government policies and incentives aimed at reducing carbon emissions. Increasing awareness of climate change, energy security concerns, and the push for sustainable development are accelerating the adoption of solar PV systems across both developed and emerging economies.
Key Highlights
- The solar photovoltaic market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 6.9% during the forecast period.
- The global solar photovoltaic market was estimated to be worth approximately USD 182.00 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach a value of USD 331.80 billion by 2032.
- The growth of the solar photovoltaic market is being driven by increasing environmental concerns, regulatory restrictions on conventional plastics, and rising consumer preference for sustainable materials across various industries.
- Based on the technology, the monocrystalline silicon segment is growing at a high rate and is projected to dominate the market.
- On the basis of grid type, the on-grid segment is projected to swipe the largest market share.
- In terms of installation, the ground mounted segment is expected to dominate the market.
- Based on the application, the residential segment is expected to dominate the market.
- By region, North America is expected to dominate the global market during the forecast period.
Solar Photovoltaic Market: Dynamics
Key Growth Drivers:
Declining Costs of Solar PV Modules and Systems
The most significant driver is the continuous and dramatic reduction in the cost of solar PV modules and complete system installations. This cost decline, driven by technological advancements, economies of scale in manufacturing, and increased competition, has made solar power highly competitive with, and often cheaper than, traditional fossil fuel-based electricity generation in many regions (achieving "grid parity" in over 70% of global electricity markets).
Supportive Government Policies and Incentives
Governments worldwide are actively promoting solar energy adoption through a range of favorable policies. These include feed-in tariffs, net metering schemes, tax credits (like the Investment Tax Credit in the U.S.), rebates, subsidies, and ambitious renewable energy targets and carbon emission reduction goals. Such policies reduce the upfront cost for consumers and investors, making solar financially attractive.
Growing Energy Demand and Energy Security Concerns
Rapid global population growth, urbanization, and industrialization are leading to a surging demand for electricity. Simultaneously, geopolitical events and volatility in fossil fuel markets highlight the importance of energy independence and security. Solar PV offers a decentralized and domestic source of power, contributing to national energy security agendas.
Restraints:
Intermittency of Solar Power and Grid Integration Challenges
Solar power generation is inherently intermittent, relying on sunlight availability (daylight hours, weather conditions). This poses challenges for grid stability and reliability, requiring significant investments in grid modernization, smart grid technologies, and energy storage solutions (batteries) to manage fluctuations, which adds to the overall system cost.
High Initial Capital Investment for Large-Scale Projects
While module costs have fallen, large-scale utility projects and even significant commercial installations still require substantial upfront capital investment. Securing financing, especially in developing markets or for innovative projects, can be a hurdle, despite various incentives available.
Land Availability and Siting Constraints
Utility-scale solar farms require significant land area, which can lead to conflicts over land use, especially in densely populated regions. Permitting processes, environmental impact assessments, and public acceptance for large projects can be time-consuming and challenging.
Opportunities:
Advancements in Energy Storage (Batteries)
The rapid development and cost reduction of battery energy storage systems (BESS), particularly lithium-ion batteries, provide a crucial solution to solar's intermittency. Integrating solar PV with storage allows for increased self-consumption, grid stability, and the ability to dispatch solar power even after sunset, opening vast new opportunities for grid-scale and residential applications.
Development of "Green" Hydrogen Production
Solar PV is a key enabler for the production of "green" hydrogen through electrolysis, which is gaining traction as a clean fuel and industrial feedstock. The falling cost of solar electricity makes it an ideal power source for electrolyzers, creating a significant new demand segment for large-scale solar projects.
Smart Grid Integration and Digitization
Opportunities lie in leveraging digital technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT for enhanced solar PV plant management. This includes AI-enabled solar forecasting for better grid integration, predictive maintenance to optimize plant uptime and reduce O&M costs, and smart grid solutions that enable more efficient energy flow and demand-side management.
Challenges:
Grid Congestion and Curtailment Risks
In regions with high solar penetration, existing grid infrastructure may not be able to handle the influx of intermittent solar power, leading to grid congestion and the need for "curtailment" (where solar power plants are instructed to reduce output). This wastes renewable energy and impacts project economics, highlighting the need for significant grid upgrades.
Securing Project Financing and Investment
While the sector is attractive, large-scale solar projects still require substantial upfront financing. Developers face challenges in securing long-term, low-cost capital, especially in markets with higher perceived risks or less stable regulatory environments.
Solar Photovoltaic Market: Report Scope
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | Solar Photovoltaic Market |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 182.00 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2032 | USD 331.80 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 6.9% |
| Number of Pages | 160 |
| Key Companies Covered | Suntech Power, Canadian Solar, Trina Solar, SunPower, Kaneka Corporation, Kyocera Corporation, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Panasonic Corporation, Sharp Corporation, JA solar Co. Ltd, Jinko Solar and ReneSola Co. Ltd |
| Segments Covered | By System, By Application, By , And By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historical Year | 2018 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2024 to 2032 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
Solar Photovoltaic Market: Segmentation Insights
The global solar photovoltaic market is divided by technology, grid type, installation, application, and region.
Based on technology, the global solar photovoltaic market is divided into monocrystalline silicon, thin film, polycrystalline silicon, and others. Monocrystalline Silicon dominates the Solar Photovoltaic Market due to its superior efficiency, space-saving attributes, and long-term reliability. Produced from a single continuous crystal structure, monocrystalline silicon cells offer higher energy conversion rates typically between 18% and 22% compared to other technologies. These panels perform better under low-light conditions and high temperatures, making them ideal for residential rooftops, commercial installations, and utility-scale solar farms where space is limited and efficiency is critical. Although more expensive to produce than polycrystalline and thin film options, their higher output and aesthetic appeal (with a uniform black appearance) continue to make monocrystalline silicon the preferred choice in both developed and emerging solar markets, especially as manufacturing costs continue to decline.
On the basis of grid type, the global solar photovoltaic market is bifurcated into on-grid and off-grid. On-grid systems dominate the Solar Photovoltaic Market, accounting for the largest share due to their widespread adoption in residential, commercial, and utility-scale installations connected directly to the public electricity grid. These systems allow users to consume electricity generated by their solar panels while exporting excess power back to the grid, often in exchange for credits or payments through net metering or feed-in tariff programs. On-grid systems are more cost-effective as they eliminate the need for battery storage and benefit from grid reliability for backup power. Governments and utilities around the world support on-grid solar adoption through subsidies, tax incentives, and renewable energy targets. This segment continues to grow rapidly, driven by falling module prices, increased electricity demand, and global decarbonization goals.
In terms of installation, the global solar photovoltaic market is bifurcated into ground mounted, rooftop, and others. Ground Mounted systems dominate the Solar Photovoltaic Market, particularly in large-scale utility and commercial installations where land availability and energy output requirements favor expansive, high-capacity solar farms. These systems are installed directly on the ground using fixed-tilt or tracking structures that optimize solar panel orientation for maximum sunlight exposure. Ground mounted PV installations benefit from ease of maintenance, scalability, and the ability to incorporate advanced tracking technologies that significantly enhance energy yield. They are preferred for utility-scale power plants, industrial facilities, and rural energy projects. With ongoing global investment in renewable energy infrastructure and utility-scale solar procurement programs especially in North America, China, India, and the Middle East ground mounted systems remain the leading installation type in terms of installed capacity and market share.
On the basis of application, the global solar photovoltaic market is bifurcated into residential, non-residential, and utilities. Utilities dominate the Solar Photovoltaic Market in terms of installed capacity and overall market share, primarily driven by large-scale solar farms and power plants developed for centralized electricity generation. Utility-scale PV projects are typically ground-mounted and connected to transmission networks to supply electricity to the grid or through power purchase agreements (PPAs). These installations benefit from economies of scale, lower cost per watt, and long-term returns through grid sales. Supported by government tenders, renewable energy targets, and international climate commitments, utility PV systems are rapidly expanding in regions such as North America, China, India, the Middle East, and Latin America. As the levelized cost of solar energy continues to fall below that of fossil fuels in many regions, utilities remain the dominant force in global solar PV deployment.
Solar Photovoltaic Market: Regional Insights
- North America is expected to dominate the global market
North America dominates the solar photovoltaic market, driven by federal and state-level incentives, corporate sustainability commitments, and expanding residential and utility-scale solar projects. The United States leads regional demand, with increasing adoption across both rooftops and large-scale solar farms. The Investment Tax Credit (ITC), net metering policies, and renewable portfolio standards (RPS) have been instrumental in supporting solar installations. Utility-scale solar has expanded rapidly in sun-rich states like California, Texas, Arizona, and Nevada, while residential solar adoption continues to grow in urban and suburban areas. Technological advancements in bifacial panels, battery storage integration, and smart inverters are further accelerating market growth. Canada is also contributing, particularly through provincial programs in Ontario and Alberta, as well as increasing interest in off-grid solar systems for remote communities and indigenous settlements.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the solar PV market, led by large-scale manufacturing, supportive government policies, and a surge in demand for clean electricity. China is the global leader in both solar PV production and deployment, with extensive utility-scale projects and distributed rooftop programs under the 14th Five-Year Plan. The country is home to the world’s largest solar farms and the majority of the world’s PV module manufacturing capacity. India is rapidly scaling up its solar infrastructure under the National Solar Mission, focusing on both ground-mounted and rooftop systems, with state-wise policies enhancing adoption. Japan and South Korea continue to deploy solar projects amid land constraints, encouraging floating PV and building-mounted installations. Southeast Asia, particularly Vietnam, Thailand, and the Philippines, is emerging as a high-potential market due to rising energy demand and policy reforms promoting solar uptake.
Europe holds a significant share in the solar PV market, supported by strong climate goals, decarbonization policies, and grid modernization efforts. Germany, Spain, Italy, and France are leading countries with well-established solar infrastructures. Germany’s feed-in tariffs and supportive regulatory environment have driven consistent deployment, particularly in residential and commercial segments. Spain and Italy are seeing a resurgence in solar development due to declining system costs and revised auction mechanisms. France continues to invest in large-scale solar and agrivoltaic systems. Across the EU, the Green Deal and REPowerEU strategies aim to rapidly scale renewable capacity, boosting demand for high-efficiency PV modules. Net-zero targets, building-integrated PV (BIPV), and solar mandates on new buildings are shaping future demand.
Solar Photovoltaic Market: Competitive Landscape
The report provides an in-depth analysis of companies operating in the solar photovoltaic market, including their geographic presence, business strategies, product offerings, market share, and recent developments. This analysis helps to understand market competition.
Some of the major players in the global solar photovoltaic market include:
- Suntech Power
- Canadian Solar
- Trina Solar
- Kaneka Corporation
- Kyocera Corporation
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Panasonic Corporation
- Sharp Corporation
- JA solar Co. Ltd
- Jinko Solar
- ReneSola Co. Ltd
- Tata Power Solar Systems Ltd.
- Wuxi Suntech Power Co. Ltd
- Nextera Energy Sources LLC
- BrightSource Energy Inc.
- SunPower Corporation
- Vivaan Solar
- Waaree Group
The global solar photovoltaic market is segmented as follows:
By Technology
- Monocrystalline Silicon
- Thin Film
- Polycrystalline Silicon
- Others
By Grid Type
- On-grid
- Off-grid
By Installation
- Ground Mounted
- Rooftop
- Others
By Application
- Residential
- Non-residential
- Utilities
By Region
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Rest of Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Table Of Content
- Chapter 1. Introduction
- 1.1. Report description and scope
- 1.2. Research scope
- 1.3. Research methodology
- 1.3.1. Market research process
- 1.3.2. Market research methodology
- Chapter 2. Executive Summary
- 2.1. Global solar PV market volume and revenue,2014 - 2020 (Mega Watt) (USD Million)
- 2.2. Global solar PV market: Snapshot
- Chapter 3. solar PV Market –Industry Analysis
- 3.1. Solar PV: Market dynamics
- 3.2. Market drivers
- 3.2.1. Global solar PV market drivers: Impact analysis
- 3.2.2. Low installation and maintenance cost
- 3.3. Market restraints
- 3.3.1. Global solar PV market restraints: Impact analysis
- 3.3.2. Irregular environmental conditions
- 3.4. Opportunities
- 3.4.1. Growing demand for solar PV installation
- 3.5. Porter’s five forces analysis
- 3.5.1. Bargaining power of suppliers
- 3.5.2. Bargaining power of buyers
- 3.5.3. Threat from new entrants
- 3.5.4. Threat from new substitutes
- 3.5.5. Degree of competition
- 3.6. Market attractiveness analysis
- 3.6.1. Market attractiveness analysis by system segment
- 3.6.2. Market attractiveness analysis by application segment
- 3.6.3. Market attractiveness analysis by regional segment
- Chapter 4. Global Solar PV Market – Competitive Landscape
- 4.1. company market share
- 4.2. Price trend Analysis
- Chapter 5. Global Solar PV Market – System Segment Analysis
- 5.1. Global solar PV market: System overview
- 5.1.1. Global solar PV market volume share by system,2014 and 2020
- 5.2. CPV
- 5.2.1. Global CPV market,2014 – 2020 (Mega Watt) (USD Million)
- 5.3. Hybrid
- 5.3.1. Global hybrid market,2014 – 2020 (Mega Watt) (USD Million)
- 5.4. Others
- 5.4.1. Global other systems market,2014 – 2020 (Mega Watt) (USD Million)
- 5.1. Global solar PV market: System overview
- Chapter 6. Global Solar PV Market – Application Segment Analysis
- 6.1. Global solar PV market: Application overview
- 6.1.1. Global solar PV market volume share by application, 2014 and 2020
- 6.2. Residential
- 6.2.1. Global solar PV market for residential,2014 – 2020 (Mega Watt) (USD Million)
- 6.3. Non-residential
- 6.3.1. Global solar PV market for non-residential,2014 – 2020 (Mega Watt) (USD Million)
- 6.4. Utility
- 6.4.1. Global solar PV market for utility,2014 – 2020 (Mega Watt) (USD Million)
- 6.1. Global solar PV market: Application overview
- Chapter 7. Global solar PV Market – Regional Segment Analysis
- 7.1. Global solar PV market: Regional overview
- 7.1.1. Global solar PV market volume share, by region, 2014 and 2020
- 7.2. North America
- 7.2.1. North America solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020, ( Mega Watt)
- 7.2.2. North America solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020, (USD Million)
- 7.2.3. North America solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.2.4. North America solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.2.5. U.S.
- 7.2.5.1. U.S. solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020 (Mega Watt)
- 7.2.5.2. U.S. solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.2.5.3. U.S. solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.2.5.4. U.S. solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.3. Europe
- 7.3.1. Europe solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020 (Mega Watt)
- 7.3.2. Europe solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.3.3. Europe solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020 (Mega Watt)
- 7.3.4. Europe solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.3.5. Germany
- 7.3.5.1. Germany solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020, ( Mega Watt)
- 7.3.5.2. Germany solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020, (USD Million)
- 7.3.5.3. Germany solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020, ( Mega Watt)
- 7.3.5.4. Germany solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020, (USD Million)
- 7.3.6. France
- 7.3.6.1. France solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020, ( Mega Watt)
- 7.3.6.2. France solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020, (USD Million)
- 7.3.6.3. France solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020, ( Mega Watt)
- 7.3.6.4. France solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020, (USD Million)
- 7.3.7. UK
- 7.3.7.1. UK solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020 (Mega Watt)
- 7.3.7.2. UK solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.3.7.3. UK solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020 (Mega Watt)
- 7.3.7.4. UK solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.4. Asia Pacific
- 7.4.1. Asia Pacific solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020 (Mega Watt)
- 7.4.2. Asia Pacific solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.4.3. Asia Pacific solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020, ( Mega Watt)
- 7.4.4. Asia Pacific solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020, (USD Million)
- 7.4.5. China
- 7.4.5.1. China solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.4.5.2. China solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.4.5.3. China solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.4.5.4. China solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.4.6. Japan
- 7.4.6.1. Japan solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.4.6.2. Japan solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.4.6.3. Japan solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.4.6.4. Japan solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.4.7. India
- 7.4.7.1. India solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.4.7.2. India solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.4.7.3. India solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.4.7.4. India solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.5. Latin America
- 7.5.1. Latin America solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.5.2. Latin America solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.5.3. Latin America solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.5.4. Latin America solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.5.5. Brazil
- 7.5.5.1. Brazil solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.5.5.2. Brazil solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.5.5.3. Brazil solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.5.5.4. Brazil solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.6. Middle East and Africa
- 7.6.1. Middle East and Africa solar PV market volume, by system,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.6.2. Middle East and Africa solar PV market revenue, by system,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.6.3. Middle East and Africa solar PV market volume, by application,2014 – 2020 ( Mega Watt)
- 7.6.4. Middle East and Africa solar PV market revenue, by application,2014 – 2020 (USD Million)
- 7.1. Global solar PV market: Regional overview
- Chapter 8. Company Profile
- 8.1. Suntech Power
- 8.1.1. Overview
- 8.1.2. Financials
- 8.1.3. System portfolio
- 8.1.4. Business strategy
- 8.1.5. Recent developments
- 8.2. Canadian Solar
- 8.2.1. Overview
- 8.2.2. Financials
- 8.2.3. System portfolio
- 8.2.4. Business strategy
- 8.2.5. Recent developments
- 8.3. Trina Solar
- 8.3.1. Overview
- 8.3.2. Financials
- 8.3.3. System portfolio
- 8.3.4. Business strategy
- 8.3.5. Recent developments
- 8.4. SunPower
- 8.4.1. Overview
- 8.4.2. Financials
- 8.4.3. System portfolio
- 8.4.4. Business strategy
- 8.4.5. Recent developments
- 8.5. Kaneka Corporation
- 8.5.1. Overview
- 8.5.2. Financials
- 8.5.3. System portfolio
- 8.5.4. Business strategy
- 8.5.5. Recent developments
- 8.6. Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 8.6.1. Overview
- 8.6.2. Financials
- 8.6.3. System portfolio
- 8.6.4. Business strategy
- 8.6.5. Recent developments
- 8.7. Panasonic Corporation
- 8.7.1. Overview
- 8.7.2. Financials
- 8.7.3. System portfolio
- 8.7.4. Business strategy
- 8.7.5. Recent developments
- 8.8. Sharp Corporation
- 8.8.1. Overview
- 8.8.2. Financials
- 8.8.3. System portfolio
- 8.8.4. Business strategy
- 8.8.5. Recent developments
- 8.9. JA solar Co. Ltd
- 8.9.1. Overview
- 8.9.2. Financials
- 8.9.3. System portfolio
- 8.9.4. Business strategy
- 8.9.5. Recent developments
- 8.10. Jinko Solar
- 8.10.1. Overview
- 8.10.2. Financials
- 8.10.3. System portfolio
- 8.10.4. Business strategy
- 8.10.5. Recent developments
- 8.1. Suntech Power
Inquiry For Buying
Solar Photovoltaic
Request Sample
Solar Photovoltaic