PSA and Membrane Separation Biogas Upgrading Market Size, Share, and Trends Analysis Report
CAGR :

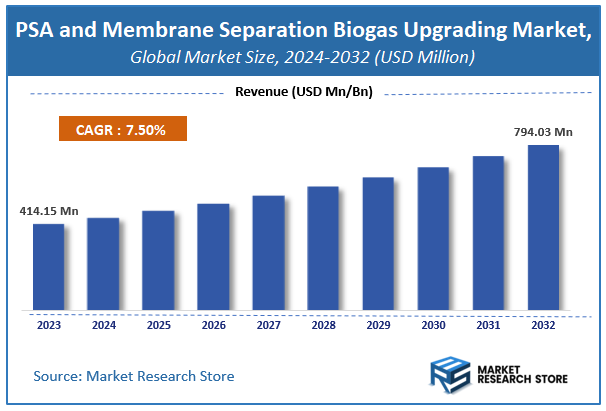
| Market Size 2023 (Base Year) | USD 414.15 Million |
| Market Size 2032 (Forecast Year) | USD 794.03 Million |
| CAGR | 7.5% |
| Forecast Period | 2024 - 2032 |
| Historical Period | 2018 - 2023 |
PSA and Membrane Separation Biogas Upgrading Market Insights
According to Market Research Store, the global PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market size was valued at around USD 414.15 million in 2023 and is estimated to reach USD 794.03 million by 2032, to register a CAGR of approximately 7.5% in terms of revenue during the forecast period 2024-2032.
The PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading report provides a comprehensive analysis of the market, including its size, share, growth trends, revenue details, and other crucial information regarding the target market. It also covers the drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges till 2032
To Get more Insights, Request a Free Sample
Global PSA and Membrane Separation Biogas Upgrading Market: Overview
Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) and membrane separation are two advanced technologies used in the biogas upgrading process, which involves purifying raw biogas to produce biomethane by removing impurities such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), water vapor, and other trace gases. PSA upgrading works on the principle of gas adsorption under pressure, where CO₂ and other contaminants are adsorbed onto a material while methane passes through.
In contrast, membrane separation relies on semi-permeable membranes that allow CO₂ and other gases to diffuse through more quickly than methane, effectively enriching the methane content in the gas stream. These technologies are crucial for transforming biogas into high-quality renewable natural gas (RNG), suitable for injection into gas grids or use as vehicle fuel.
Key Highlights
- The PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period.
- The global PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market was estimated to be worth approximately USD 414.15 million in 2023 and is projected to reach a value of USD 794.03 million by 2032.
- The growth of the PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market is being driven by increasing demand for clean energy, supportive government regulations promoting renewable energy, and a global shift toward sustainable waste management.
- Based on the technology, the pressure swing adsorption (PSA) segment is growing at a high rate and is projected to dominate the market.
- On the basis of feedstock type, the organic waste segment is projected to swipe the largest market share.
- In terms of application, the power generation segment is expected to dominate the market.
- Based on the end-user, the energy sector segment is expected to dominate the market.
- Based on the scale of operation, the large scale segment is expected to dominate the market.
- By region, Europe is expected to dominate the global market during the forecast period.
PSA and Membrane Separation Biogas Upgrading Market: Dynamics
Key Growth Drivers:
Rising Demand for Renewable Energy: Governments and industries are increasingly shifting toward low-carbon, eco-friendly energy solutions. Biogas, when upgraded through PSA or membrane technologies, becomes biomethane — a renewable substitute for natural gas, driving its global demand.
Supportive Government Policies and Incentives: Financial support like subsidies, tax benefits, and renewable energy targets are encouraging investments in biogas upgrading infrastructure. Such policies make adoption more viable and attractive to project developers.
Technological Advancements: Continuous innovation in PSA and membrane separation technologies has led to better gas purity, higher methane recovery rates, and improved cost-efficiency, making these systems more competitive and scalable.
Growing Waste-to-Energy Projects: With rising municipal and agricultural waste, countries are investing in waste-to-energy systems. Biogas plants equipped with upgrading technologies convert waste into clean fuel, promoting a circular economy.
Restraints:
High Initial Investment Costs: Installing PSA or membrane separation units involves substantial upfront capital for equipment, infrastructure, and integration, which can limit adoption by small-scale producers or in developing markets.
Operational and Maintenance Complexity: Advanced biogas upgrading systems demand skilled personnel for regular monitoring, calibration, and maintenance. This complexity can increase operating costs and limit widespread deployment.
Opportunities:
Expansion in Emerging Economies: Developing countries with large agricultural bases and rising energy needs present a huge potential market. Investments in rural biogas systems are opening doors for scalable upgrading solutions.
Integration with Natural Gas Grids: Upgraded biogas can be directly injected into existing gas pipelines, enabling broader use as a renewable fuel and reducing dependence on fossil natural gas.
Carbon Credit and Green Certification: Producers of upgraded biogas can benefit from carbon trading mechanisms and green certifications, which not only generate revenue but also support sustainability branding.
Challenges:
Feedstock Quality and Supply Variability: Fluctuations in the type and quality of organic material used for biogas production can affect the consistency of raw biogas, complicating the upgrading process.
Competition from Other Renewable Technologies: The rapid growth of solar, wind, and green hydrogen markets can divert attention and investment away from biogas, making it harder for upgrading technologies to secure funding.
Lack of Awareness and Skilled Workforce: Limited understanding of biogas upgrading benefits and a shortage of trained technicians, especially in remote or underdeveloped regions, hinder broader market adoption.
PSA and Membrane Separation Biogas Upgrading Market: Report Scope
This report thoroughly analyzes the PSA and Membrane separation biogas upgrading market, exploring its historical trends, current state, and future projections. The market estimates presented result from a robust research methodology, incorporating primary research, secondary sources, and expert opinions. These estimates are influenced by the prevailing market dynamics as well as key economic, social, and political factors. Furthermore, the report considers the impact of regulations, government expenditures, and advancements in research and development on the market. Both positive and negative shifts are evaluated to ensure a comprehensive and accurate market outlook.
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
|---|---|
| Report Name | PSA and Membrane Separation Biogas Upgrading Market |
| Market Size in 2023 | USD 414.15 Million |
| Market Forecast in 2032 | USD 794.03 Million |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 7.5% |
| Number of Pages | 150 |
| Key Companies Covered | Inova BioMethan, Pentair Haffmans, Air Liquide, Greenmac, EnviTec Biogas, Beijing Sanyl, Bright Biomethane, Xebec, Carbotech Gas, Guild Associates, NeoZeo AB, ETW Energietechnik, Mahler AGS, Sysadvance |
| Segments Covered | By Technology Type, By Feedstock Type, By Application, By End-User, By Scale of Operation, and By Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Latin America, Middle East, and Africa (MEA) |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Historical Year | 2018 to 2023 |
| Forecast Year | 2024 to 2032 |
| Customization Scope | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. Request For Customization |
PSA and Membrane Separation Biogas Upgrading Market: Segmentation Insights
The global PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market is divided by technology type, feedstock type, application, end-user, scale of operation, and region.
Segmentation Insights by Technology Type
Based on technology type, the global PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market is divided into pressure swing adsorption (PSA), membrane separation, and absorption.
In the PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market, Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) technology holds the position as the most dominant segment. PSA is widely adopted due to its efficiency in separating carbon dioxide (CO₂) from methane (CH₄) in biogas, enabling the production of high-purity biomethane. The process operates through a cycle of pressurization and depressurization using adsorbent materials that selectively retain CO₂ while allowing methane to pass through. PSA systems are especially favored in medium to large-scale biogas plants due to their reliability, cost-effectiveness over time, and the ability to deliver methane with high purity levels suitable for injection into natural gas grids or for use as vehicle fuel.
Membrane Separation follows PSA in terms of market share and is steadily gaining traction, especially in decentralized or smaller biogas production facilities. This technology employs semi-permeable membranes that allow selective permeation of CO₂ over CH₄ based on molecular size and solubility differences. Membrane systems are compact, modular, and relatively easy to maintain, making them ideal for flexible applications and installations with limited space. Moreover, they can be easily scaled and integrated with other technologies, offering a lower environmental footprint and reduced energy consumption compared to traditional methods.
Absorption, although less dominant, still plays a notable role in the market, particularly in older biogas upgrading installations or in cases where water or chemical absorption is already integrated into the process. This method typically involves using water or a chemical solvent to absorb CO₂ from the raw biogas stream. Despite being effective, absorption systems generally require more operational oversight, greater water or chemical usage, and can incur higher long-term operational costs. Consequently, its market share has been declining in favor of more modern, efficient technologies like PSA and membrane separation.
Segmentation Insights by Feedstock Type
On the basis of feedstock type, the global PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market is bifurcated into organic waste, agricultural residues, sewage sludge, and landfill gas.
In the PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market, Organic Waste is the most dominant feedstock type driving biogas production. This category includes food waste, industrial organic by-products, and other biodegradable municipal solid waste. Its dominance is attributed to the increasing availability of organic waste in urban areas and supportive regulatory frameworks promoting waste-to-energy solutions. Biogas derived from organic waste typically contains a relatively high concentration of methane, making it an ideal input for upgrading technologies like PSA and membrane separation. Governments and municipalities worldwide are investing in infrastructure to divert organic waste from landfills toward biogas production, further solidifying this segment's leading role.
Agricultural Residues represent the second most significant segment in this market. These residues include crop waste, manure, and other farm by-products, which are abundant in rural and farming-intensive regions. The biogas produced from these sources is often used on-site in farms or agricultural communities, and the increasing interest in sustainable farming practices is accelerating the adoption of upgrading technologies. Though the methane content can vary depending on the specific residue used, advancements in pre-treatment and digestion technologies have enhanced the efficiency of upgrading biogas from agricultural residues.
Sewage Sludge is another noteworthy feedstock, especially in urban settings where wastewater treatment plants generate large volumes of sludge as a by-product. This sludge can be anaerobically digested to produce biogas, which is then upgraded using PSA or membrane separation. Although the overall biogas yield from sewage sludge may be lower compared to organic or agricultural waste, the constant and predictable supply from municipal sources makes it a stable feedstock for biogas upgrading projects.
Landfill Gas, while still relevant, is the least dominant feedstock in the biogas upgrading market. Although landfills produce significant volumes of gas through the natural decomposition of waste, the methane concentration in landfill gas is typically lower and less consistent than that from other feedstocks. Additionally, environmental regulations are increasingly focused on reducing landfill dependency, which indirectly affects the growth potential of this segment. As a result, landfill gas is gradually being overshadowed by more sustainable and efficient sources like organic and agricultural waste.
Segmentation Insights by Application
On the basis of application, the global PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market is bifurcated into power generation, transport fuel, grid injection, industrial applications, and heating.
In the PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market, Power Generation stands as the most dominant application. Upgraded biogas, or biomethane, is widely used in combined heat and power (CHP) systems to generate electricity and heat simultaneously. This application is especially prevalent in areas with supportive energy policies and incentives aimed at reducing fossil fuel dependency. The consistent energy output and ability to feed electricity directly into local grids make power generation a highly attractive option for both public utilities and private operators. Moreover, the ability to co-generate heat adds to the overall efficiency of the system, further driving adoption.
Transport Fuel is emerging as a rapidly growing application and holds the second spot in terms of dominance. Biomethane serves as a renewable alternative to diesel and gasoline, particularly for buses, trucks, and municipal vehicles. This segment is gaining momentum due to stricter vehicle emission regulations, carbon reduction targets, and increasing investment in renewable fuels infrastructure. In regions like Europe and parts of North America, compressed biomethane (Bio-CNG) and liquefied biomethane (Bio-LNG) are being adopted widely in the transportation sector.
Grid Injection is also a significant application, especially in countries with well-established gas grid networks. Upgraded biogas is purified to natural gas quality and injected into the grid, helping to decarbonize the gas supply. This application supports the integration of renewable energy into national energy mixes and provides flexibility in energy use. However, it ranks slightly below transport fuel in dominance due to the regulatory complexity and infrastructure requirements associated with grid compatibility and safety standards.
Industrial Applications form a moderate share of the market, where biomethane is used as a substitute for natural gas in various industrial processes such as heating, drying, and chemical production. While industries are increasingly looking to reduce their carbon footprint, adoption depends heavily on economic incentives, energy prices, and the scale of operations. As such, this application is more niche but growing steadily with the global push for decarbonization in the industrial sector.
Heating, while relevant, is the least dominant application in this market. Though biomethane can be used for residential and commercial space heating or water heating, it often competes with other renewable heating options like heat pumps and solar thermal systems. Additionally, the cost-effectiveness and infrastructure availability for biogas-based heating vary greatly by region, which limits its widespread adoption compared to other applications.
Segmentation Insights by End-User
On the basis of end-user, the global PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market is bifurcated into energy sector, transportation sector, agriculture, municipalities, and chemical manufacturing.
In the PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market, the Energy Sector is the most dominant end-user. This sector extensively utilizes upgraded biogas for electricity generation and grid injection, aligning with global efforts to transition toward renewable energy sources. Power utilities and energy companies are adopting PSA and membrane technologies to convert raw biogas into high-purity biomethane, which can be used in combined heat and power (CHP) plants or injected into natural gas networks. The energy sector's dominance is further supported by policy incentives, carbon reduction goals, and the strategic integration of biomethane into national energy strategies.
The Transportation Sector follows closely behind and is rapidly gaining ground. With growing global interest in alternative fuels, especially for heavy-duty and public transport, biomethane is being increasingly adopted as a clean, low-carbon fuel. Compressed biomethane (Bio-CNG) and liquefied biomethane (Bio-LNG) are fueling buses, trucks, and even ships in some regions. Governments and private fleets are investing in biogas fueling infrastructure, pushing this sector to become one of the fastest-growing end-users of upgraded biogas technologies.
Agriculture is a significant end-user, especially in rural and farming communities where agricultural residues and animal manure are abundant feedstocks for biogas production. Farmers are adopting biogas upgrading systems to generate revenue from waste, reduce energy costs, and produce on-site fuel or electricity. Although often on a smaller scale compared to the energy and transport sectors, the agricultural segment plays a vital role in circular economy initiatives and decentralized energy production.
Municipalities also represent a key end-user group, leveraging upgraded biogas from organic municipal solid waste and sewage sludge. City governments and local utilities are using PSA and membrane technologies in waste-to-energy projects, wastewater treatment plants, and landfill gas recovery systems. While municipalities are influential in promoting sustainable waste management practices, their adoption levels vary based on local policies, funding availability, and infrastructure.
Chemical Manufacturing, though the least dominant, is an emerging end-user of upgraded biogas. Biomethane can be used as a feedstock or process gas in chemical production, especially in operations aiming to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. However, this segment is still relatively niche due to the complexity of integration, higher purity requirements, and limited awareness compared to more traditional applications.
Segmentation Insights by Scale of Operation
On the basis of scale of operation, the global PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market is bifurcated into small scale, medium scale, large scale, and commercial scale.
In the PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market, the Large Scale segment is the most dominant in terms of scale of operation. These facilities are typically part of centralized biogas plants, municipal waste management systems, or industrial operations with high biogas output. They rely on PSA or membrane technologies to handle high volumes of biogas efficiently and produce biomethane suitable for grid injection or industrial use. The economic viability of large-scale operations is enhanced by economies of scale, consistent feedstock supply, and integration with existing energy infrastructure, making them attractive to energy utilities and municipalities.
The Commercial Scale segment closely follows, consisting of facilities developed primarily for profit and often integrated into the renewable energy or waste-to-energy markets. These operations can vary in size but are characterized by standardized, reliable output and supply agreements with utilities or fuel distributors. Commercial biogas upgrading projects are often backed by private investment and benefit from policy support such as feed-in tariffs, subsidies, or carbon credits. Their flexibility in catering to both power generation and transport fuel applications strengthens their position in the market.
Medium Scale operations are typically found in agricultural cooperatives, small industrial parks, or regional wastewater treatment facilities. These installations strike a balance between capacity and investment, making them suitable for localized energy generation or vehicle fuel use. As technology becomes more affordable and modular, medium-scale projects are growing in popularity, particularly in areas aiming to decentralize energy production.
Small Scale systems represent the least dominant segment. These are often used in individual farms, small communities, or pilot projects and are ideal for on-site use of biogas, such as heating or electricity generation. While PSA and membrane technologies are being adapted for smaller systems, the higher relative cost and maintenance complexity can be a barrier. However, as modular and containerized systems become more accessible, the adoption of upgrading technology at the small scale is expected to grow, especially in rural or off-grid settings.
PSA and Membrane Separation Biogas Upgrading Market: Regional Insights
- Europe is expected to dominates the global market
Europe is the most dominant region in the PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market. This dominance is largely due to the region's strong regulatory framework promoting renewable energy adoption and emission reduction. Countries like Germany, France, Sweden, and the United Kingdom have developed extensive biogas infrastructure, especially for upgrading technologies that allow biomethane to be injected into the national gas grid or used as vehicle fuel. The maturity of the biogas sector, combined with favorable policies and significant public and private investments, solidifies Europe's leading position.
North America follows as a key player in the market, experiencing robust growth due to rising investments in renewable natural gas (RNG) infrastructure and supportive legislative frameworks. The United States and Canada are actively expanding their biogas upgrading capacity, driven by renewable portfolio standards, tax credits, and low-carbon fuel standards. The demand for sustainable fuel alternatives, particularly in the transportation sector, also drives the adoption of membrane and PSA technologies in this region.
Asia-Pacific is rapidly emerging in the market, supported by increasing urbanization, industrial activity, and a growing need for clean energy solutions. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are expanding their biogas production capacities while integrating upgrading technologies to improve energy efficiency. National policies focused on reducing fossil fuel dependency and promoting sustainable waste management play a critical role in driving market adoption across the region.
Latin America is gradually expanding its presence in the biogas upgrading market, fueled by a focus on diversifying energy sources and improving waste-to-energy systems. Nations like Brazil, Argentina, and Chile are leveraging their abundant agricultural and organic waste resources to boost biogas production. While the upgrading segment is still developing, growing environmental awareness and supportive policy measures are starting to stimulate adoption.
Middle East and Africa remain the least developed regions in the PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market. However, there is growing recognition of the importance of sustainable energy solutions, especially in urban centers and areas facing waste management challenges. Although projects remain limited and mostly in pilot stages, the long-term potential is promising as governments and private entities begin to explore biogas upgrading technologies for energy diversification and environmental sustainability.
PSA and Membrane Separation Biogas Upgrading Market: Competitive Landscape
The report provides an in-depth analysis of companies operating in the PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market, including their geographic presence, business strategies, product offerings, market share, and recent developments. This analysis helps to understand market competition.
Some of the major players in the global PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market include:
- Inova BioMethan
- Pentair Haffmans
- Air Liquide
- Greenmac
- EnviTec Biogas
- Beijing Sanyl
- Bright Biomethane
- Xebec
- Carbotech Gas
- Guild Associates
- NeoZeo AB
- ETW Energietechnik
- Mahler AGS
- Sysadvance
The global PSA and membrane separation biogas upgrading market is segmented as follows:
By Technology Type
- Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA)
- Membrane Separation
- Absorption
By Feedstock Type
- Organic Waste
- Agricultural Residues
- Sewage Sludge
- Landfill Gas
By Application
- Power Generation
- Transport Fuel
- Grid Injection
- Industrial Applications
- Heating
By End-User
- Energy Sector
- Transportation Sector
- Agriculture
- Municipalities
- Chemical Manufacturing
By Scale of Operation
- Small Scale
- Medium Scale
- Large Scale
- Commercial Scale
By Region
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- U.K.
- France
- Germany
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Rest of Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
- GCC Countries
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Table Of Content
Inquiry For Buying
PSA and Membrane Separation Biogas Upgrading
Request Sample
PSA and Membrane Separation Biogas Upgrading
